Intergenerational impact of maternal obesity and postnatal feeding practices on pediatric obesity
- PMID: 24147925
- PMCID: PMC4123431
- DOI: 10.1111/nure.12054
Intergenerational impact of maternal obesity and postnatal feeding practices on pediatric obesity
Abstract
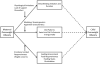
The postnatal feeding practices of obese and overweight mothers may place their children at increased risk for the development of obesity through shared biology and family environments. This article reviews the feeding practices of obese mothers, describes the potential mechanisms linking maternal feeding behaviors to child obesity risk, and highlights the potential avenues of intervention. Strategies important for improving the quality of the eating environment and preventing the intergenerational transmission of obesity include supporting breastfeeding, improving the food choices of obese women, and encouraging the development of feeding styles that are responsive to hunger and satiety cues.
Keywords: maternal feeding behaviors; obese mothers; pediatric obesity; postnatal feeding practices.
© 2013 International Life Sciences Institute.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal intuitive eating as a moderator of the association between concern about child weight and restrictive child feeding.Appetite. 2015 Dec;95:158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2015.06.023. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Appetite. 2015. PMID: 26145275 Free PMC article.
-
Eating, feeding, and feeling: emotional responsiveness mediates longitudinal associations between maternal binge eating, feeding practices, and child weight.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2016 Aug 2;13:89. doi: 10.1186/s12966-016-0415-5. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2016. PMID: 27484590 Free PMC article.
-
Caregiver feeding practices and child weight outcomes: a systematic review.Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Mar 1;109(Suppl_7):990S-1002S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy276. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30982865
-
Maternal concern and perception about child overweight risk, maternal feeding practices, and child eating behaviors: A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 11;19(6):e0302557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302557. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38861515 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Predictors of Child Dietary Behaviors and Weight Status.Curr Nutr Rep. 2018 Dec;7(4):268-273. doi: 10.1007/s13668-018-0250-1. Curr Nutr Rep. 2018. PMID: 30350172 Review.
Cited by
-
Pregnancy and post-delivery maternal weight changes and overweight in preschool children.Prev Med. 2014 Mar;60:77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2013.12.018. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Prev Med. 2014. PMID: 24370455 Free PMC article.
-
High sugar content and body mass index: modelling pathways around the first 1000 d of life, BRISA cohort.Public Health Nutr. 2021 Oct;24(15):4997-5005. doi: 10.1017/S136898002000525X. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Public Health Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33517949 Free PMC article.
-
Grandmaternal obesity in early pregnancy and risk of grandoffspring preterm birth: a nationwide three-generation study.Int J Obes (Lond). 2025 May;49(5):942-948. doi: 10.1038/s41366-025-01731-7. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Int J Obes (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39948389
-
Maternal Pre-Pregnancy BMI, Offspring Adiposity in Late Childhood, and Age of Weaning: A Causal Mediation Analysis.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 29;15(13):2970. doi: 10.3390/nu15132970. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447295 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Diet During Pregnancy and Lactation and Child Food Preferences, Dietary Patterns, and Weight Outcomes: a Review of Recent Research.Curr Nutr Rep. 2021 Dec;10(4):413-426. doi: 10.1007/s13668-021-00366-0. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Curr Nutr Rep. 2021. PMID: 34383279 Review.
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. Jama. 2010 Jan 20;303(3):235–241. - PubMed
-
- Chu SY, Kim SY, Bish CL. Prepregnancy obesity prevalence in the United States, 2004-2005. Matern Child Health J. 2009 Sep;13(5):614–620. - PubMed
-
- Oken E. Maternal and child obesity: the causal link. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2009 Jun;36(2):361–377. ix-x. - PubMed
-
- Poston L. Maternal obesity, gestational weight gain and diet as determinants of offspring long term health. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2012 - PubMed
-
- Rooney K, Ozanne SE. Maternal over-nutrition and offspring obesity predisposition: targets for preventative interventions. Int J Obes (Lond) 2011 Jul;35(7):883–890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

