The role of 14,15-dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid levels in inflammation and its relationship to lipoproteins
- PMID: 24148690
- PMCID: PMC3874761
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-151
The role of 14,15-dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid levels in inflammation and its relationship to lipoproteins
Abstract
Background: 14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (14,15-EETs) generated from arachidonic acid by cytochrome P450 epoxygenases have beneficial effects in certain cardiovascular diseases, and increased 14,15-EET levels protect the cardiovascular system. 14,15-EETs are rapidly hydrolyzed by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) to the corresponding 14,15-dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (14,15-DHETs), which are generally less biologically active but more stable metabolite. A functionally relevant polymorphism of the CYP2J2 gene is independently associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), and the major CYP2J2 product is 14,15-EETs. 14,15-DHETs can be considered a relevant marker of CYP2J2 activity. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the plasma 14,15-DHET levels to reflect the 14,15-EET levels in an indirectly way in patients with CHD, and to highlight the growing body of evidence that 14,15-EETs also play a role in anti-inflammatory and lipid-regulating effects in patients with CHD. This was achieved by investigating the relationship between 14,15-DHETs and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and blood lipoproteins.
Methods: Samples of peripheral venous blood were drawn from 60 patients with CHD and 60 healthy controls. A 14,15-DHET enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (14,15-DHET ELISA kit) was used to measure the plasma 14,15-DHET levels. Hs-CRP, total cholesterol, triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels were measured.
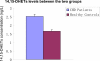
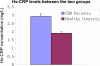
Results: 14,15-DHET levels (2.53 ± 1.60 ng/mL) were significantly higher in patients with CHD as compared with those of the healthy controls (1.65 ± 1.54 ng/mL, P < 0.05). There was a significant positive correlation between 14,15-DHETs and hs-CRP levels (R = 0.286, P = 0.027). However, there was no significant correlation between 14,15-DHETs and blood lipoproteins (all, P > 0.05).
Conclusions: Increased plasma 14,15-DHET levels reflect the decreased of 14,15-EET levels in an indirectly way. Indicated that decreased plasma 14,15-EET levels might be involved in the inflammatory reaction process in atherosclerosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids are potent vasodilators in the canine coronary microcirculation.Circ Res. 1998 Nov 2;83(9):932-9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.83.9.932. Circ Res. 1998. PMID: 9797342
-
Increases in levels of epoxyeicosatrienoic and dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs and DHETs) in liver and heart in vivo by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and in hepatic EET:DHET ratios by cotreatment with TCDD and the soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor AUDA.Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Feb;42(2):294-300. doi: 10.1124/dmd.113.055368. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014. PMID: 24311719 Free PMC article.
-
14,15-Dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 Jan;290(1):H55-63. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00427.2005. Epub 2005 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16113065
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid pathway in human health and diseases.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;61(3):188-96. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e318273b007. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23011468 Review.
-
Cytochrome P450 epoxygenases, soluble epoxide hydrolase, and the regulation of cardiovascular inflammation.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Feb;48(2):331-41. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.10.022. Epub 2009 Nov 3. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 19891972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidized Products of Omega-6 and Omega-3 Long Chain Fatty Acids Are Associated with Increased White Matter Hyperintensity and Poorer Executive Function Performance in a Cohort of Cognitively Normal Hypertensive Older Adults.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;74(1):65-77. doi: 10.3233/JAD-191197. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32176647 Free PMC article.
-
The role of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in the cardiovascular system.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;80(1):28-44. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12603. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25655310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs) and Eicosanoids on Dry Eye Symptoms and Signs.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 20;14(3):376. doi: 10.3390/biom14030376. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540794 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydroxyeicosatrienoic Acid, a Metabolite of Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids Upregulates Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression Through Transcription: Mechanism of Vascular Endothelial Function Protection.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Jun;79(2):289-299. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-00978-x. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33811614
-
CYP2C19 Contributes to THP-1-Cell-Derived M2 Macrophage Polarization by Producing 11,12- and 14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid, Agonists of the PPARγ Receptor.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 15;16(4):593. doi: 10.3390/ph16040593. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Michaelis UR, Fisslthaler B. et al.Cytochrome P450 2C9-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids induce angiogenesis via cross-talk with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) FASEB J. 2003;17(6):770–772. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick FA, Ennis MD. et al.Inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity and platelet aggregation by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Influence of stereochemistry. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:15334–15338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

