SET for life: biochemical activities and biological functions of SET domain-containing proteins
- PMID: 24148750
- PMCID: PMC3941473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.09.004
SET for life: biochemical activities and biological functions of SET domain-containing proteins
Abstract
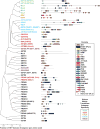
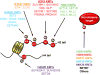
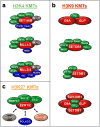
SET domain-containing proteins belong to a group of enzymes named after a common domain that utilizes the cofactor S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to achieve methylation of its substrates. Many SET domain-containing proteins have been shown to display catalytic activity towards particular lysine residues on histones, but emerging evidence also indicates that various non-histone proteins are specifically targeted by this clade of enzymes. Here, we summarize the most recent findings on the biological functions of the major families of SET domain-containing proteins catalyzing the methylation of histones 3 on lysines 4, 9, 27, and 36 (H3K4, H3K9, H3K27, and H3K36) and histone 4 on lysine 20 (H4K20) as well as candidates that have been reported to regulate non-histone substrates.
Keywords: SET domain-containing proteins; histone lysine methylation; non-histone substrates.
Figures
References
-
- Schneider J, et al. Molecular regulation of histone H3 trimethylation by COMPASS and the regulation of gene expression. Molecular cell. 2005;19:849–856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

