Effects of stabilization exercise using a ball on mutifidus cross-sectional area in patients with chronic low back pain
- PMID: 24149162
- PMCID: PMC3772599
Effects of stabilization exercise using a ball on mutifidus cross-sectional area in patients with chronic low back pain
Abstract
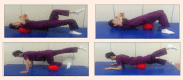
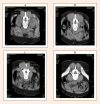
The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of lumbar stabilization exercises using balls to the effects of general lumbar stabilization exercises with respect to changes in the cross section of the multifidus (MF), weight bearing, pain, and functional disorders in patients with non-specific chronic low back pain. Twelve patients participated in either a 8 week (3 days per week) stabilization exercise program using balls and control group (n = 12). The computer tomography (CT) was used to analyze MF cross-sectional areas (CSA) and Tetrax balancing scale was used to analyze left and right weight bearing differences. Both groups had significant changes in the CSA of the MF by segment after training (p < 0.05) and the experimental group showed greater increases at the L4 (F = 9.854, p = 0.005) and L5 (F = 39. 266, p = 0.000). Both groups showed significant decreases in weight bearing, from 9.25% to 5.83% in the experimental group and from 9.33% to 4.25% in the control group (p < 0.05), but did not differ significantly between the two groups. These results suggests that stabilization exercises using ball can increases in the CSA of the MF segments, improvement in weight bearing, pain relief, and recovery from functional disorders, and the increases in the CSA of the MF of the L4 and L5 segments for patients with low back pain. Key PointsCompared with the stabilization exercise using a ball and general stabilization exercise increased the CSA of the MF, weight bearing, pain, and functional ability in patients with low back pain.We verified that increases in the CSA of the MF of the L4 and L5 segments and functional ability during the stabilization exercise using a ball.The stabilization exercise using a ball was shown to be an effective exercise method for patients with low back pain in a rehabilitation program by increasing functional ability and the CSA of the MF.
Keywords: Stabilization exercise; ball; cross-sectional area; low back pain; multifidus.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander K.M., LaPier T.L. (1998) Differences in static balance and weight distribution between normal subjects and subjects with chronic unilateral low back pain. Physical Therapy Journal of Orthopedic & Sports Physical Therapy 28(6), 378-383 - PubMed
-
- Anderson K., Behm D.G. (2005) Trunk muscle activity increases with unstable squat movements. Canadian Journal of Applied Physiology 30(1), 33-45 - PubMed
-
- Beneck G.J., Kulig K. (2012) Multifidus atrophy is localized and bilateral in active persons with chronic unilateral low back pain. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 93(2), 300-306 - PubMed
-
- Bennell K.L., Goldie P.A. (1994) The differential effects of external ankle support on postural control. Physical Therapy Journal of Orthopedic & Sports Physical Therapy 20(6), 287-295 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical