Effects of Whole-body Vibration Training on Sprint Running Kinematics and Explosive Strength Performance
- PMID: 24149223
- PMCID: PMC3778698
Effects of Whole-body Vibration Training on Sprint Running Kinematics and Explosive Strength Performance
Abstract
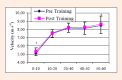
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of 6 wk of whole body vibration (WBV) training on sprint running kinematics and explosive strength performance. Twenty-four volunteers (12 women and 12 men) participated in the study and were randomised (n = 12) into the experimental and control groups. The WBV group performed a 6-wk program (16-30 min·d(-1), 3 times a week) on a vibration platform. The amplitude of the vibration platform was 2.5 mm and the acceleration was 2.28 g. The control group did not participate in any training. Tests were performed Pre and post the training period. Sprint running performance was measured during a 60 m sprint where running time, running speed, step length and step rate were calculated. Explosive strength performance was measured during a counter movement jump (CMJ) test, where jump height and total number of jumps performed in a period of 30 s (30CVJT). Performance in 10 m, 20 m, 40 m, 50 m and 60 m improved significantly after 6 wk of WBV training with an overall improvement of 2.7%. The step length and running speed improved by 5.1% and 3.6%, and the step rate decreased by 3.4%. The countermovement jump height increased by 3.3%, and the explosive strength endurance improved overall by 7.8%. The WBV training period of 6 wk produced significant changes in sprint running kinematics and explosive strength performance. Key pointsWBV training.Sprint running kinematics.Explosive strength performance.
Keywords: Sprinting kinematics; counter-movement jump; explosive strength; strength training.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of warm-up methods on strength-speed for sprinters in athletics: a mini review.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 Feb 27;6:1360414. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1360414. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 38476581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The short-term effect of whole-body vibration training on vertical jump, sprint, and agility performance.J Strength Cond Res. 2004 Nov;18(4):828-32. doi: 10.1519/14213.1. J Strength Cond Res. 2004. PMID: 15574090 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of 40-m repeated sprint training on maximum sprinting speed, repeated sprint speed endurance, vertical jump, and aerobic capacity in young elite male soccer players.J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Sep;25(9):2364-70. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182023a65. J Strength Cond Res. 2011. PMID: 21869624 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute effect of whole-body vibration on sprint and jumping performance in elite skeleton athletes.J Strength Cond Res. 2008 Jul;22(4):1371-4. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e31816a44b5. J Strength Cond Res. 2008. PMID: 18545165
-
The effects of repeated-sprint training on field-based fitness measures: a meta-analysis of controlled and non-controlled trials.Sports Med. 2015 Jun;45(6):881-91. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0324-9. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 25790793 Review.
Cited by
-
A comparison of the effect of a variety of thermal and vibratory modalities on skin temperature and blood flow in healthy volunteers.Med Sci Monit. 2011 Sep;17(9):MT72-81. doi: 10.12659/msm.881921. Med Sci Monit. 2011. PMID: 21873956 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of warm-up methods on strength-speed for sprinters in athletics: a mini review.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 Feb 27;6:1360414. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1360414. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 38476581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Countermovement Jump Performance in First Position (Sauté) in Healthy Adults.Sports Health. 2019 Mar/Apr;11(2):186-191. doi: 10.1177/1941738118824569. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Sports Health. 2019. PMID: 30676874 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of whole-body vibration frequency and amplitude on the myoelectric activity of vastus medialis and vastus lateralis.J Sports Sci Med. 2011 Mar 1;10(1):169-74. eCollection 2011. J Sports Sci Med. 2011. PMID: 24149311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosco C., Cardinale M., Tsarpela O. (1999a) Influence of vibration on mechanical power and electromyogram activity in human arm flexor muscles. European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology 779, 306-311 - PubMed
-
- Bosco C., Colli R., Introini E. (1999b) Adaptive responses of human skeletal muscle to vibration exposure. Clinical Physiology 119, 83-187 - PubMed
-
- Bosco C., Cardinale M., Tsarpela O., Colli R., Tihanyi J., Von Duvil-lard S., Viru A. (1998) The influence of whole body vibration on the mechanical behaviour of skeletal muscle. Biology of Sport 153, 157-164
-
- Bosco C., Luhtanen P., Komi P. (1983) A simple method for measurement of mechanical power in jumping. European Journal of Applied Physiology 550, 273-282 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources