MRI Findings Do not Correlate with Outcome in Athletes with Chronic Groin Pain
- PMID: 24149227
- PMCID: PMC3778702
MRI Findings Do not Correlate with Outcome in Athletes with Chronic Groin Pain
Abstract
This trial aimed to assess the value of MRI in the differential diagnosis of chronic groin pain in athletes, a condition caused by various pathologies, the most common being posterior abdominal wall deficiency, osteitis pubis and muscular imbalance. Nineteen subjects with clinically ruled-out hernia and recurrent episodes of exercise-triggered groin pain were assessed. Dynamic MRI was performed under Valsalva manoeuver and at rest within a training- free period and after training activity. Follow-up was performed after 4 years using a questionnaire and physical examination. An incipient hernia was seen in one case, Valsalva manoeuver provoked a visible bulging in 7 others (3 bilateral). Eight athletes showed symphysitis (accompanied by bulging in 3 cases). MRI visualized one hydrocele, one osteoma of the left femur, one enchondroma of the pubic bone, and one dilated left ureter without clinical symptoms or therapeutic relevance. MRI findings after training and during the training free period did not vary. Fifteen participants were available for a follow-up control examination 4 years later - one suffered from ongoing pain, eleven were free of symptoms and three had improvement. However, most of them improved only with changing or reducing training. There were four participants with a specific therapy of their MRI findings. MRI revealed a variety of pathological findings in athletes suffering from chronic groin pain, but it was not reliable enough in differentiating between diagnoses requiring conservative or operative treatment. The MRI examination within the training interval did not have an advantage to that within the training-free period. Further randomized prospective trials with a long follow-up should establish whether MRI findings could be of help in the choice between conservative and surgical treatment for chronic groin pain. Key pointsMRI findings after training and during the train free period did not vary.MRI revealed a variety of pathological findings in athletes suffering from chronic groin pain, but it was not reliable enough in differentiating between diagnoses requiring conservative or operative treatment.
Keywords: MRI; athletes; chronic groin pain; hernia; symphysitis.
Figures
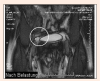
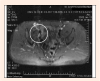
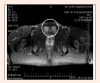

Similar articles
-
[Groin pain in athletes: role of magnetic resonance].Radiol Med. 2000 Oct;100(4):216-22. Radiol Med. 2000. PMID: 11155446 Italian.
-
Laparoscopic surgery for chronic groin pain in athletes is more effective than nonoperative treatment: a randomized clinical trial with magnetic resonance imaging of 60 patients with sportsman's hernia (athletic pubalgia).Surgery. 2011 Jul;150(1):99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.02.016. Epub 2011 May 5. Surgery. 2011. PMID: 21549403 Clinical Trial.
-
Osteitis pubis in professional football players: MRI findings and correlation with clinical outcome.Eur J Radiol. 2017 Sep;94:46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.07.009. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Eur J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28941759
-
[Groin pain in athletes-sportsmen's groin].Radiologie (Heidelb). 2023 Apr;63(4):268-274. doi: 10.1007/s00117-023-01117-8. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Radiologie (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 36715718 Review. German.
-
Athletic osteitis pubis.Sports Med. 2011 May 1;41(5):361-76. doi: 10.2165/11586820-000000000-00000. Sports Med. 2011. PMID: 21510714 Review.
Cited by
-
Groin hernia diagnostics: dynamic inguinal ultrasound (DIUS).Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017 Nov;402(7):1039-1045. doi: 10.1007/s00423-017-1604-7. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017. PMID: 28812139
-
Long-standing groin pain in contact sports: a prospective case-control and MRI study.BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2019 Mar 19;5(1):e000507. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2018-000507. eCollection 2019. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2019. PMID: 31191965 Free PMC article.
-
The cleft sign may be an independent factor of magnetic resonance imaging findings associated with a delayed return-to-play time in athletes with groin pain.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 May;29(5):1474-1482. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06410-w. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 33452578
-
Athletic Pubalgia in Females: Predictive Value of MRI in Outcomes of Endoscopic Surgery.Orthop J Sports Med. 2017 Aug 3;5(8):2325967117720171. doi: 10.1177/2325967117720171. eCollection 2017 Aug. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28840145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akita K., Niga S., Yamato Y., Muneta T., Sato T. (1999) Anatomic basis of chronic groin pain with special reference to sports hernia. Surgical and Radiologic Anatomie 21, 1-5 - PubMed
-
- Barry N.N., McGuire J.L. (1996) Acute injuries and specific problems in adult athletes. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America 22, 531-549 - PubMed
-
- Cabot J.R. (1966) Osteopatica dinamica del pubis. In: Proceedings of the XVI World Congress of Sports Medicine. Hannover, Deutscher Aerztverlag. Ed:Hanekopf G.359-364
-
- Edelman D.S., Selesnick H. (2006) “Sports” hernia: treatment with biologic mesh (Surgisis): A preliminary study. Surgical Endoscopy 20, 971-973 - PubMed
-
- Ekberg O., Sjoberg S., Westlin N. (1996) Sports-related groin pain: evaluation with MR imaging. European Radiology, 6, 52-55 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
