The effects of intermittent hypoxic training on aerobic capacity and endurance performance in cyclists
- PMID: 24149312
- PMCID: PMC3737917
The effects of intermittent hypoxic training on aerobic capacity and endurance performance in cyclists
Abstract
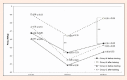
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy of intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) with 95 % of lactate threshold workload (WRLT) on aerobic capacity and endurance performance in well-trained cyclists. Twenty male elite cyclists, randomly divided into a hypoxia (H) group (n=10; age 22 ± 2.7years; VO2max 67.8 ± 2.5 ml·kg(-1)·min(-1); body height (BH) 1.78 ± 0.05 m; body mass (BM) 66.7 ± 5.4kg; fat free mass (FFM) 59.3 ± 5.1kg; fat content (FAT%) 11.3 ± 2.1%), and a control (C) group (n = 10; age 23.5 ± 3. 5years; VO2max 67.7 ± 2.0 ml·kg(-1)·min(-1); BH 1.79 ± 3.2 m; BM 69.2 ± 5.5 kg; FFM 63.6 ± 4.8 kg; FAT% 7.9 ± 1.94 %) took part in the research project. The training program used during the experiment was the same for the both groups. For three weeks, the subjects in H group performed 3 training sessions per week in normobaric hypoxia environment (IHT - O2 = 15. 2%). During the elemental core of the IHT session, the intensity was set at 95% WRLT for 30-min in 1(st) microcycle, 35-min in 2(nd) microcycle and 40-min in 3(rd) microcycle. The same training procedure was provided in C group, yet the intensity of the main sessions were set at 100% WRLT in the normoxia environment. The results indicate a significant (p < 0.05) increase in VO2max,VO2LT, WRmax, WRLT and change in lactate concentration (∆LA) during incremental test in H group. Also a significant (p < 0.05) decrease in time of the time trial was seen, associated with a significant increase (p < 0.05) in average generated power (Pavg) and average speed (Vavg) during the time trial. The intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) applied in this research did not significantly affect the hematological variables considered: number of erythrocytes (RBC), hemoglobin concentration (HGB) and haematocrit value (HCT). Significant blood value increases (p < 0.05) were only observed in MCV in H group. This data suggests that intermittent hypoxic training at lactate threshold intensity and medium duration (30-40min) is an effective training means for improving aerobic capacity and endurance performance at sea level. Key pointsThe efficacy of the intermittent hypoxic training is mostly dependent on volume and intensity of exercise in the hypoxic environment.The observed results suggests that intermittent hypoxic training at lactate threshold intensity and medium duration (30-40min) is an effective training means for improving aerobic capacity and endurance performance at sea level.
Keywords: Intermittent hypoxic training (IHT); aerobic capacity; cycling; endurance performance; hypoxia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the effect of intermittent hypoxic training vs. the live high, train low strategy on aerobic capacity and sports performance in cyclists in normoxia.Biol Sport. 2018 Mar;35(1):39-48. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2018.70750. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Biol Sport. 2018. PMID: 30237660 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of high intensity interval training in normobaric hypoxia on aerobic capacity in basketball players.J Hum Kinet. 2013 Dec 31;39:103-14. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2013-0073. eCollection 2013 Dec 18. J Hum Kinet. 2013. PMID: 24511346 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent Hypoxic Training at Lactate Threshold Intensity Improves Aiming Performance in Well-Trained Biathletes with Little Change of Cardiovascular Variables.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Sep 25;2019:1287506. doi: 10.1155/2019/1287506. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31662969 Free PMC article.
-
Combining hypoxic methods for peak performance.Sports Med. 2010 Jan 1;40(1):1-25. doi: 10.2165/11317920-000000000-00000. Sports Med. 2010. PMID: 20020784 Review.
-
Advancing hypoxic training in team sports: from intermittent hypoxic training to repeated sprint training in hypoxia.Br J Sports Med. 2013 Dec;47 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i45-50. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-092741. Br J Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 24282207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Four-week "living high training low" program enhances 3000-m and 5000-m time trials by improving energy metabolism during submaximal exercise in athletes.J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2017 Mar 31;21(1):1-6. doi: 10.20463/jenb.2017.0060. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28712259 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of three weeks base training at moderate simulated altitude with or without hypoxic residence on exercise capacity and physiological adaptations in well-trained male runners.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 29;12:e17166. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17166. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38563004 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Natural or Simulated Altitude Training on High-Intensity Intermittent Running Performance in Team-Sport Athletes: A Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2018 Feb;48(2):431-446. doi: 10.1007/s40279-017-0809-9. Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 29129021 Review.
-
The relationship between hemoglobin and : A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 12;18(10):e0292835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292835. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37824583 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic Intermittent Hypoxic Training Is Not Beneficial for Maximal Oxygen Uptake and Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2025 Jun;35(6):e70088. doi: 10.1111/sms.70088. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2025. PMID: 40548904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonnetti D.L., Hopkins W.G., Kilding A.E. (2006) High-intensity kayak performance after adaptation to intermittent hypoxia. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance 1, 246-260 - PubMed
-
- Cheng B., Kuipers H., Snyder A.C., Keizer H.A., Jeukendrup A., Hesselink M. (1992) A new approach for the determination of ventilator and lactate thresholds. International Journal of Sport Medicine 13, 518-522 - PubMed
-
- Clark S.A., Aughey R.J., Gore C.J., Hahn A.G., Townsend N.E., Kinsman T.A., Chow C.M., McKenna M.J., Hawley J.A. (2004) Effects of live high, train low hypoxic exposure on lactate metabolism in trained humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 96, 517-525 - PubMed
-
- Czuba M., Zajac A., Cholewa J., Poprzecki S., Waskiewicz Z. (2009) Lactate threshold (D-max method) and maximal lactate steady-state in cyclists. Journal of Human Kinetics 21, 49-56
-
- Desplanches D., Hoppeler H. (1993) Effects of training in normoxia and normobaric hypoxia on human muscle ultrastructure. Pflügers Archiv European Journal of Physiology 425, 263-267 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous