Exercise performance and muscle contractile properties after creatine monohydrate supplementation in aerobic-anaerobic training rats
- PMID: 24149473
- PMCID: PMC3794480
Exercise performance and muscle contractile properties after creatine monohydrate supplementation in aerobic-anaerobic training rats
Abstract
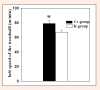
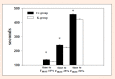
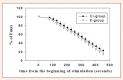
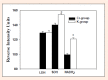
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of creatine monohydrate supplementation on exercise performance and contractile variables in aerobic-anaerobic training rats. Twenty 90-day-old male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into two groups - creatine (Cr) and controls (K). The creatine group received creatine monohydrate as a nutritional supplement, whereas the control group was given placebo. Both groups were trained 5 days a week on a treadmill for 20 days in a mixed (aerobic-anaerobic) metabolic working regimen (27 m·min(-1), 15% elevation for 40 min). The exercise performance (sprint-test), contractile properties (m. tibialis anterior), oxidative enzyme activity (SDH, LDH, NADH2) in m. soleus and blood hematological and chemical variables were assessed in the groups at the end of the experiment. It was found out that creatine supplementation improved the exercise performance after 20 days of administration in a dose of 60 mg per day on the background of a mixed (aerobic-anaerobic) exercise training. At the end of the trial the Cr-group demonstrated better values for the variables which characterize the contractile properties of m. tibialis anterior containing predominantly types IIA and IIB muscle fibers. On the other hand, a higher oxidative capacity was found out in m. soleus (type I muscle fibers) as a result of 20-day creatine supplementation. No side effects of creatine monohydrate supplementation were assessed by the hematological and blood biochemical indices measured in this study. Key pointsThe creatine monohydrate supplementation of the rats diet improves their exercise performance after 20 days administration in a dose of 60 mg per day on the background of a mixed (aerobic-anaerobic) exercise training.The creatine supplemented rats demonstrate better contractile properties of m. tibialis anterior which muscle contains predominantly types IIA and IIB muscle fibers.The soleus muscle (type I muscle fibers) demonstrates a higher oxidative capacity as a result of 20-days creatine supplementation.
Keywords: Exercise; creatine supplementation; muscle contractile properties; performance; rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Creatine supplementation induces alteration in cross-sectional area in skeletal muscle fibers of wistar rats under swimming training.J Sports Sci Med. 2002 Sep 1;1(3):87-95. eCollection 2002 Sep. J Sports Sci Med. 2002. PMID: 24701129 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of creatine supplementation on aerobic performance and anaerobic capacity in elite rowers in the course of endurance training.Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2003 Jun;13(2):173-83. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.13.2.173. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2003. PMID: 12945828 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of creatine supplementation on muscle metabolic response to a maximal treadmill exercise test in Standardbred horses.Equine Vet J. 2000 Nov;32(6):533-40. doi: 10.2746/042516400777584578. Equine Vet J. 2000. PMID: 11093628
-
Effects of Creatine Monohydrate on Endurance Performance in a Trained Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2023 May;53(5):1017-1027. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01823-2. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 36877404
-
Creatine as nutritional supplementation and medicinal product.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2001 Mar;41(1):1-10. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2001. PMID: 11317142 Review.
References
-
- Chwalbinska-Moneta J. (2003) Effect of creatine supplementation on aerobic performance and anaerobic capacity in elite rowers in the course of endurance training. International Journal of Sports Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism 13, 173-183 - PubMed
-
- Dawson B., Cutler M., Moody A., Lawrence S., Doodman C., Randall N. (1995) The effect of oral creatine loading on single and repeated maximal short sprints. Australian Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 27, 56-61 - PubMed
-
- Delp M.D., Duan C. (1996) Composition and size of type I, IIA, IID/X, and IIB fibers and citrate synthase activity of rat muscle. Journal of Applied Physiology 80, 261-270 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
