Accuracy of the Polar S810i(TM) Heart Rate Monitor and the Sensewear Pro Armband(TM) to Estimate Energy Expenditure of Indoor Rowing Exercise in Overweight and Obese Individuals
- PMID: 24149647
- PMCID: PMC3761702
Accuracy of the Polar S810i(TM) Heart Rate Monitor and the Sensewear Pro Armband(TM) to Estimate Energy Expenditure of Indoor Rowing Exercise in Overweight and Obese Individuals
Abstract
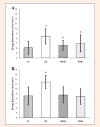
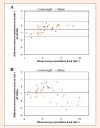
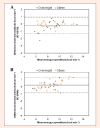
Accurately assessing the energy expenditure (EE) of different types of physical activity is important for exercise prescription in obese individuals. The aim of this study was to examine the accuracy of the Polar S810i Heart Rate Monitor and SenseWear Pro Armband (SWA) for estimating energy expenditure (EE) during indoor rowing versus indirect calorimetry (IC). 43 overweight and obese adults (16 men, 27 women, BMI = 31.2 ± 3.7) participated in the study. Within a week after a maximal incremental test on a rowing ergometer, EE was assessed with Polar S810i, SWA and IC during two different intensities of rowing exercises (at 50% VO2max and 70% VO2max) on a Concept II ergometer. Data were analyzed with Pearson's product moment correlations and repeated measures ANOVA. Post hoc multiple comparisons were performed using the Bonferroni test. Bland-Altman plots were created to assess the agreement between the EE estimates and IC measurements. At 50% VO2max, Polar S810i and SWA significantly overestimated EE by 0.5 ± 0.50 kcal·min(-1) (p < 0.001) and by 0.9 ± 0.92 kcal·min(-1) (p < 0.001), respectively. At 70% VO2max, no significant differences were found between the SWA and IC, and between Polar S810i and IC measurements. Bland-Altman plots showed good agreements between the measured EE and estimates by Polar S810i and SWA at 70% VO2max. At 50% VO2max, there was a poor agreement between SWA and IC measurements. There were high correlations among three methods at both intensities (r = 0.82 to r = 0.95). In conclusion, Polar S810i and SWA showed reasonable concordance with IC for measuring EE of the moderate intensity exercise but not the lower intensity exercise on indoor rowing in the participants of this study. Polar S810i and SWA might be useful to assess EE during indoor rowing for overweight and obese individuals who try to manage their body weight, but it is necessary to develop exercise and population specific algorithms to enhance the accuracy of SWA to estimate energy expenditure during various intensities of physical exercises. Key pointsPolar S810i and SWA when compared to the indirect calorimetry, provide reasonable estimates of energy expenditure on rowing ergometer at the moderate exercise intensity, but not at the low exercise intensity.The monitor of the Concept II Model D rowing ergometer significantly overestimated the energy expenditure during low and moderate intensity exercises. However there was a moderate correlation between EE estimates of this device and indirect calorimetry measurements.
Keywords: Indirect calorimetry; armband; energy expenditure; heart rate monitor; indoor rowing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validity of Accelerometers for the Evaluation of Energy Expenditure in Obese and Overweight Individuals: A Systematic Review.J Nutr Metab. 2020 Aug 4;2020:2327017. doi: 10.1155/2020/2327017. eCollection 2020. J Nutr Metab. 2020. PMID: 32832147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validity of a multi-sensor armband in estimating rest and exercise energy expenditure.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004 Jun;36(6):1063-9. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000128144.91337.38. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004. PMID: 15179178
-
Validation of the SenseWear Pro3 Armband using an incremental exercise test.J Strength Cond Res. 2014 Oct;28(10):2806-14. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182a1f836. J Strength Cond Res. 2014. PMID: 25250859
-
Evaluation of a multisensor armband in estimating energy expenditure in obese individuals.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006 Dec;14(12):2217-23. doi: 10.1038/oby.2006.260. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006. PMID: 17189549
-
Monitoring Energy Expenditure Using a Multi-Sensor Device-Applications and Limitations of the SenseWear Armband in Athletic Populations.Front Physiol. 2017 Nov 30;8:983. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00983. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29249986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Energy expenditure during gait in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis.Acta Ortop Bras. 2013 Mar;21(2):116-9. doi: 10.1590/S1413-78522013000200009. Acta Ortop Bras. 2013. PMID: 24453654 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of Accelerometers for the Evaluation of Energy Expenditure in Obese and Overweight Individuals: A Systematic Review.J Nutr Metab. 2020 Aug 4;2020:2327017. doi: 10.1155/2020/2327017. eCollection 2020. J Nutr Metab. 2020. PMID: 32832147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimized Nutrition in Mitochondrial Disease Correlates to Improved Muscle Fatigue, Strength, and Quality of Life.Neurotherapeutics. 2023 Oct;20(6):1723-1745. doi: 10.1007/s13311-023-01418-9. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Neurotherapeutics. 2023. PMID: 37723406 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet and Exercise: Effect of a 10-Week Intervention on Body Composition and CVD Risk Factors in Overweight and Obese Women-A Randomized Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 30;13(1):110. doi: 10.3390/nu13010110. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33396889 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of SenseWear® Armband v5.2 and v2.2 for estimating energy expenditure.J Sports Sci. 2016 Oct;34(19):1830-8. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2016.1140220. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Sports Sci. 2016. PMID: 26854829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borg G.(1982) Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 14, 377-381 - PubMed
-
- Calle E.E., Thun M.J., Petrelli J.M., Rodriguez C., Heath C.W.(1999) Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of U.S. adults. The New England Journal of Medicine 341, 1097-1105 - PubMed
-
- Campbell K.L., Crocker P.R., Mc Kenzie D.C.(2002) Field evaluation of energy expenditure in women using Tritrac accelerometers. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 34, 1667-1674 - PubMed
-
- Cole P.J., LeMura L.M., Klinger T.A., Strohecker K., Mc Connell T.R.(2004)Measuring energy expenditure in cardiac patients using the Body Media Armband versus indirect calorimetry. A validation study Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness. 44(3), 262-271 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
