A codon-optimized bacterial antibiotic gene used as selection marker for stable nuclear transformation in the marine red alga Pyropia yezoensis
- PMID: 24149658
- PMCID: PMC3996358
- DOI: 10.1007/s10126-013-9549-5
A codon-optimized bacterial antibiotic gene used as selection marker for stable nuclear transformation in the marine red alga Pyropia yezoensis
Abstract
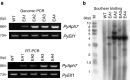
Marine macroalgae play an important role in marine coastal ecosystems and are widely used as sea vegetation foodstuffs and for industrial purposes. Therefore, there have been increased demands for useful species and varieties of these macroalgae. However, genetic transformation in macroalgae has not yet been established. We have developed a dominant selection marker for stable nuclear transformation in the red macroalga Pyropia yezoensis. We engineered the coding region of the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene aph7″ from Streptomyces hygroscopicus to adapt codon usage of the nuclear genes of P. yezoensis. We designated this codon-optimized aph7″ gene as PyAph7. After bombarding P. yezoensis cells with plasmids containing PyAph7 under the control of their endogenous promoter, 1.9 thalli (or individuals) of hygromycin-resistant strains were isolated from a 10-mm square piece of the bombarded thallus. These transformants were stably maintained throughout the asexual life cycle. Stable expression of PyAph7was verified using Southern blot analysis and genomic PCR and RT-PCR analyses. PyAph7 proved to be a new versatile tool for stable nuclear transformation in P. yezoensis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stable nuclear transformation of Gonium pectorale.BMC Biotechnol. 2009 Jul 10;9:64. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-9-64. BMC Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19591675 Free PMC article.
-
An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Protist. 2002 Dec;153(4):401-12. doi: 10.1078/14344610260450136. Protist. 2002. PMID: 12627869
-
Stable nuclear transformation of Eudorina elegans.BMC Biotechnol. 2013 Feb 12;13:11. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-11. BMC Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23402598 Free PMC article.
-
A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Gene. 2001 Oct 17;277(1-2):221-9. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00616-3. Gene. 2001. PMID: 11602359
-
Advances of selectable marker genes in plastid genetic engineering.Yi Chuan. 2017 Sep 20;39(9):810-827. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.16-433. Yi Chuan. 2017. PMID: 28936979 Review.
Cited by
-
Stable Nuclear Transformation System for the Coccolithophorid Alga Pleurochrysis carterae.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 7;6:22252. doi: 10.1038/srep22252. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26947136 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of Plastid Expression Vector and Development of Genetic Transformation System for the Seaweed Pyropia yezoensis.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017 Apr;19(2):147-156. doi: 10.1007/s10126-017-9736-x. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017. PMID: 28233074
-
Genome editing in macroalgae: advances and challenges.Front Genome Ed. 2024 Mar 6;6:1380682. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2024.1380682. eCollection 2024. Front Genome Ed. 2024. PMID: 38516199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and characterization of a spore development mutant in Pyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta) induced via insertional mutagenesis.J Phycol. 2025 Aug;61(4):805-819. doi: 10.1111/jpy.70026. Epub 2025 May 5. J Phycol. 2025. PMID: 40323712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asamizu E, Nakajima M, Kitade Y, Saga N, Nakamura Y, Tabata S. Comparison of RNA expression profiles between the two generations of Porphyra yezoensis (Rhodophyta), based on expressed sequence tag frequency analysis. J Phycol. 2003;39:923–930. doi: 10.1046/j.1529-8817.2003.03003.x. - DOI
-
- Choi HS, Choi KH, Rhew TH. Simple and rapid isolation of plasmids from Porphyra tenera. Algae. 2000;15:133–136.
-
- Choi HS, Choi KH, Kim TH, Lee CH, Rhew TH. Characterization of natural plasmid and construction of putative transformation vector using the plasmid in Korean red alga, Porphyra tenera. Algae. 2001;16:287–294.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
