Influence of nanosecond pulsed laser irradiance on the viability of nanoparticle-loaded cells: implications for safety of contrast-enhanced photoacoustic imaging
- PMID: 24150862
- PMCID: PMC3916331
- DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/46/465101
Influence of nanosecond pulsed laser irradiance on the viability of nanoparticle-loaded cells: implications for safety of contrast-enhanced photoacoustic imaging
Abstract
Photoacoustic imaging, a promising new diagnostic medical imaging modality, can provide high contrast images of molecular features by introducing highly-absorbing plasmonic nanoparticles. Currently, it is uncertain whether the absorption of low fluence pulsed light by plasmonic nanoparticles could lead to cellular damage. In our studies we have shown that low fluence pulsed laser excitation of accumulated nanoparticles at low concentration does not impact cell growth and viability, while we identify thresholds at which higher nanoparticle concentrations and fluences produce clear evidence of cell death. The results provide insights for improved design of photoacoustic contrast agents and for applications in combined imaging and therapy.
Figures
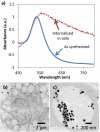
 ), 12 mJ/cm2 (
), 12 mJ/cm2 ( ), 23 mJ/cm2 (
), 23 mJ/cm2 ( ), and 36 mJ/cm2 (
), and 36 mJ/cm2 ( ). (n = 6 microplate wells)
). (n = 6 microplate wells)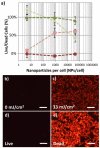
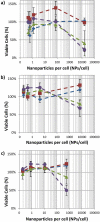
 ), and EthD-III (dead stain), (
), and EthD-III (dead stain), ( ), of macrophage cells incubated with 50 nm gold spheres remains unchanged with increasing concentrations of NPs per cell when no laser is applied. After 1000 pulses of 29 mJ/cm2 laser fluence, significant changes in the percentage of macrophage cells living, (
), of macrophage cells incubated with 50 nm gold spheres remains unchanged with increasing concentrations of NPs per cell when no laser is applied. After 1000 pulses of 29 mJ/cm2 laser fluence, significant changes in the percentage of macrophage cells living, ( ), and dead, (
), and dead, ( ), are seen at NPs concentrations which are greater than 880 NPs/cell. (n = 6 microplate wells) The presence of a large population of dead cells stained by EthD-III after laser fluence is confirmed by fluorescence microscopy (b,c). The cells shown are MDA-MB-435 cells with 8200 NPs/cell. The fluorescent microscopy images of control cell populations which were not loaded with nanoparticles, one untreated (“Live”, d) and treated with 70% ethanol (“Dead”, e) are shown. Images obtained using a 20× objective (0.5 NA) and Leica 6000 DM microscope. Scale bars are 50 μm.
), are seen at NPs concentrations which are greater than 880 NPs/cell. (n = 6 microplate wells) The presence of a large population of dead cells stained by EthD-III after laser fluence is confirmed by fluorescence microscopy (b,c). The cells shown are MDA-MB-435 cells with 8200 NPs/cell. The fluorescent microscopy images of control cell populations which were not loaded with nanoparticles, one untreated (“Live”, d) and treated with 70% ethanol (“Dead”, e) are shown. Images obtained using a 20× objective (0.5 NA) and Leica 6000 DM microscope. Scale bars are 50 μm.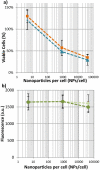
 ), or 24 hours after laser exposure, (
), or 24 hours after laser exposure, ( ), does not change the number of viable cells. Likewise, b) shows that the presence of apoptotic cell markers cannot be detected at either 0 mJ/cm2, (
), does not change the number of viable cells. Likewise, b) shows that the presence of apoptotic cell markers cannot be detected at either 0 mJ/cm2, ( ) or 33 mJ/cm2, (
) or 33 mJ/cm2, ( ). (n = 6 microplate wells)
). (n = 6 microplate wells)References
-
- American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers. Laser Institute of America; 2007.
-
- Agarwal A, Huang SW, O'Donnell M, Day KC, Day M, Kotov N, Ashkenazi S. Targeted gold nanorod contrast agent for prostate cancer detection by photoacoustic imaging. J. Appl. Phys. 2007;102
-
- Albanese A, Tang PS, Chan WCW. The Effect of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Surface Chemistry on Biological Systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012;14:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Au L, Chen J, Wang LV, Xia Y. Gold nanocages for cancer imaging and therapy Methods. Mol. Biol. 2010;624:83–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
