Renal prognosis a long time after renal biopsy on patients with diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 24151019
- PMCID: PMC3888309
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gft349
Renal prognosis a long time after renal biopsy on patients with diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
Background: A new classification of diabetic nephropathy was reported by Tervaert et al., but the association between pathological findings and the clinical outcomes remains unclear.
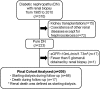
Methods: Among 310 patients with diabetes mellitus who underwent renal biopsy from March 1985 to January 2010 and were confirmed to have diabetic nephropathy according to the Tervaert's classification, 205 patients were enrolled in this study. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was used to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for death-censored renal death. Each regression analysis employed two levels of multivariate adjustment.
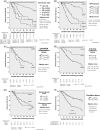
Results: After adjustment for age, gender, estimated glomerular filtration rate, type of diabetes, urinary protein excretion, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, HbA1c, diabetic retinopathy and red blood cells in urinary sediment at the time of renal biopsy, compared with glomerular class IIA, the HRs for death-censored renal death of glomerular classes I, IIB, III and IV were 0.21 (95% CI: 0.04-1.25), 2.12 (0.89-5.04), 4.23 (1.80-9.90), and 3.27 (1.32-8.10), respectively. Also, compared with an interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy score 1 group, HRs for score 0 group, score 2 group and score 3 group were 0.08 (0.01-0.57), 2.17 (0.96-4.91), 4.78 (1.96-11.68), respectively.
Conclusions: The progression of glomerular, tubulointerstitial and vascular lesions was associated with higher HRs for renal death. These results suggest the clinical utility of Tervaert's pathological classification.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy; pathological classification; renal prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical implications of linear immunofluorescent staining for immunoglobulin G in patients with diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014 Dec;106(3):522-30. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.09.051. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 25458334
-
A pathological scoring system to predict renal outcome in diabetic nephropathy.Am J Nephrol. 2015;41(4-5):337-44. doi: 10.1159/000431333. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Am J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26067713
-
Histological predictors for renal prognosis in diabetic nephropathy in diabetes mellitus type 2 patients with overt proteinuria.Nephrology (Carlton). 2012 Jan;17(1):68-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2011.01525.x. Nephrology (Carlton). 2012. PMID: 21933307
-
Lessons learned from studies of the natural history of diabetic nephropathy in young type 1 diabetic patients.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008 Aug;5 Suppl 4:958-63. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18806710 Review.
-
Histopathology of diabetic nephropathy.Semin Nephrol. 2007 Mar;27(2):195-207. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2007.01.012. Semin Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17418688 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modified arteriosclerosis score predicts the outcomes of diabetic kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2021 Aug 18;22(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02492-x. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34407751 Free PMC article.
-
A clinicopathological study of renal biopsies from 288 elderly patients: analysis based on 4,185 cases.Int Urol Nephrol. 2015 Feb;47(2):327-33. doi: 10.1007/s11255-014-0895-7. Epub 2014 Dec 25. Int Urol Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25539617
-
Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Syndrome Rather Than a Single Disease.Rev Diabet Stud. 2015 Spring-Summer;12(1-2):87-109. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2015.12.87. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Rev Diabet Stud. 2015. PMID: 26676663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney biopsy can help to predict renal outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2025 Jan;44(1):91-101. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.23.059. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 38212871 Free PMC article.
-
C3c deposition predicts worse renal outcomes in patients with biopsy-proven diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes. 2022 Apr;14(4):291-297. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13264. Epub 2022 Mar 24. J Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35322566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, et al. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009;301:2129–2140. - PubMed
-
- Cowie CC, Port FK, Wolfe RA, et al. Disparities in incidence of diabetic end-stage renal disease according to race and type of diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1074–1079. - PubMed
-
- Ritz E, Orth SR. Nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1127–1133. - PubMed
-
- Wada T, Shimizu M, Toyama T, et al. Clinical impact of albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012;16:96–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

