Immunostaining of p16(INK4a)/Ki-67 and L1 capsid protein on liquid-based cytology specimens obtained from ASC-H and LSIL-H cases
- PMID: 24151431
- PMCID: PMC3804785
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.6526
Immunostaining of p16(INK4a)/Ki-67 and L1 capsid protein on liquid-based cytology specimens obtained from ASC-H and LSIL-H cases
Abstract
Background: Atypical squamous cell cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASC-H) and low-grade intraepithelial lesion cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL-H) are ambiguous diagnostic entities for the prediction of high-grade cervical lesion. Objective and reproducible tests for predicting high-grade cervical lesions are needed to reduce unnecessary colposcopic referrals or follow-ups.
Objective: We aimed to identify an adequate set of adjunctive markers to predict cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2+ (CIN2+) in residual liquid-based cytology specimens (LBCS).
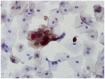
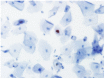
Methods: We conducted p16 (INK4a)/Ki-67 and L1 capsid protein immunostaining and human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA typing on 56 LBCS diagnosed with ASC-H or LSIL-H, all of which were subjected to histologic confirmation or follow-up cytologic examination.
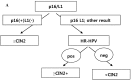
Results: Positivity for p16 (INK4a)/Ki-67 was associated with a histology of CIN2+ (P=0.047) and CIN3+ (P=0.002). Negativity for L1 capsid protein was associated with CIN2+ confirmed at follow-up (P=0.02).Positivity for high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) was associated with CIN2+ confirmed at follow-up (P=0.036) and a histology of CIN2+ (P=0.037). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value for predicting follow-up CIN2+ were 76.2%, 51.4%, 48.5%, and 78.3%, respectively, for p16 (INK4a)/Ki-67 immunostaining; 95.2%, 34.3%, 46.5%, and 92.3%, respectively, for L1 capsid protein; and 66.7%, 67.7%, 54.5%, and 77.8%, respectively, for HR-HPV. The classification and regression tree analysis showed that the combined results of p16 (INK4a)/Ki-67 andL1 capsid protein immunostaining and the HR-HPV test, conducted sequentially, correctly classified 81.8% of samples (27/33)in the prediction of a histology of CIN2 + in ASC-H or LSIL-H. For determination of the histology of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3+ (CIN3+)in ASC-H or LSIL-H, we found that the combined results of p16 (INK4a)/Ki-67 and L1 capsid protein immunostaining correctly classified 78.8% (26/33) of samples.
Conclusions: p16(INK4a)/Ki-67 and L1 capsid protein immunostaining and HR-HPV testing of residual LBCS diagnosed with ASC-H or LSIL-H are useful objective biomarkers for predicting CIN2+. Immunostaining for p16(INK4a)/Ki-67 and L1 capsid protein are sufficient to predict CIN3+.
Keywords: Cervicovaginal cytology; HPV DNA typing.; Human papillomavirus; Immunocytochemistry; L1 capsid protein; p16 INK4a/Ki-67 dual staining.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide incidence of eighteen major cancers in 1985. Int J Cancer. 1993;54:594–606. - PubMed
-
- Denny L. The prevention of cervical cancer in developing countries. BJOG. 2005;112:1204–12. - PubMed
-
- Walboomers JM, Jacobs MV, Manos MM. et al. Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J Pathol. 1999;189:12–9. - PubMed
-
- Steben M, Duarte-Franco E. Human papillomavirus infection: epidemiology and pathophysiology. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;107:S2–5. - PubMed
-
- Ostör AG. Natural history of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: a critical review. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1993;12:186–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

