Absence of detectable HIV-1 viremia after treatment cessation in an infant
- PMID: 24152233
- PMCID: PMC3954754
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1302976
Absence of detectable HIV-1 viremia after treatment cessation in an infant
Abstract
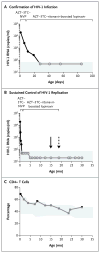
An infant born to a woman with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection began receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) 30 hours after birth owing to high-risk exposure. ART was continued when detection of HIV-1 DNA and RNA on repeat testing met the standard diagnostic criteria for infection. After therapy was discontinued (when the child was 18 months of age), levels of plasma HIV-1 RNA, proviral DNA in peripheral-blood mononuclear cells, and HIV-1 antibodies, as assessed by means of clinical assays, remained undetectable in the child through 30 months of age. This case suggests that very early ART in infants may alter the establishment and long-term persistence of HIV-1 infection.
Figures
Comment in
-
Baby steps on the road to HIV eradication.N Engl J Med. 2013 Nov 7;369(19):1855-7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1309006. Epub 2013 Oct 23. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24152231 No abstract available.
-
Absence of HIV-1 after treatment cessation in an infant.N Engl J Med. 2014 Feb 13;370(7):678. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1315498. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24521123 No abstract available.
-
Absence of HIV-1 after treatment cessation in an infant.N Engl J Med. 2014 Feb 13;370(7):678. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1315498. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24521124 No abstract available.
References
-
- UNAIDS. World AIDS Day global report. 2012 ( http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/campaigns/20121120_globalreport2012)
-
- Hütter G, Nowak D, Mossner M, et al. Long-term control of HIV by CCR5 Delta32/Delta32 stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:692–8. - PubMed
-
- Allers K, Hütter G, Hofmann J, et al. Evidence for the cure of HIV infection by CCR5 Delta32/Delta32 stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2011;117:2791–9. - PubMed
-
- Guidelines for the use of anti-retroviral agents in pediatric HIV infection. Rockville, MD: AIDSinfo; 2012. Panel on Antiretroviral Therapy and Medical Management of HIV-Infected Children. ( http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/2/pediatric-treatment-guidelines/0)
-
- FDA Drug Safety Communication. Serious health problems seen in premature babies given Kaletra (lopinavir/ritonavir) oral solution. Silver Spring, MD: Food and Drug Administration; 2011. ( http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm246002.htm)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI080193/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000161/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- AI306214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI042845/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI096113/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI093701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI080193/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000161/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI042845/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI100656/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1-AI-068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI062446/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HD0577849/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI74621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI93701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI074621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI096113/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
