A comparative study of ribosomal proteins: linkage between amino acid distribution and ribosomal assembly
- PMID: 24152303
- PMCID: PMC4016315
- DOI: 10.1186/2046-1682-6-13
A comparative study of ribosomal proteins: linkage between amino acid distribution and ribosomal assembly
Abstract
Background: Assembly of the ribosome from its protein and RNA constituents must occur quickly and efficiently in order to synthesize the proteins necessary for all cellular activity. Since the early 1960's, certain characteristics of possible assembly pathways have been elucidated, yet the mechanisms that govern the precise recognition events remain unclear.We utilize a comparative analysis to investigate the amino acid composition of ribosomal proteins (r-proteins) with respect to their role in the assembly process. We compared small subunit (30S) r-protein sequences to those of other housekeeping proteins from 560 bacterial species and searched for correlations between r-protein amino acid content and factors such as assembly binding order, environmental growth temperature, protein size, and contact with ribosomal RNA (rRNA) in the 30S complex.
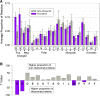
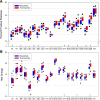
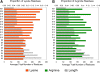
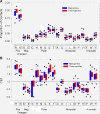
Results: We find r-proteins have a significantly high percent of positive residues, which are highly represented at rRNA contact sites. An inverse correlation between the percent of positive residues and r-protein size was identified and is mainly due to the content of Lysine residues, rather than Arginine. Nearly all r-proteins carry a net positive charge, but no statistical correlation between the net charge and the binding order was detected. Thermophilic (high-temperature) r-proteins contain increased Arginine, Isoleucine, and Tyrosine, and decreased Serine and Threonine compared to mesophilic (lower-temperature), reflecting a known distinction between thermophiles and mesophiles, possibly to account for protein thermostability. However, this difference in amino acid content does not extend to rRNA contact sites, as the proportions of thermophilic and mesophilic contact residues are not significantly different.
Conclusions: Given the significantly higher level of positively charged residues in r-proteins and at contact sites, we conclude that ribosome assembly relies heavily on an electrostatic component of interaction. However, the binding order of r-proteins in assembly does not appear to depend on these electrostatics interactions. Additionally, because thermophiles and mesophiles exhibit significantly different amino acid compositions in their sequences but not in the identities of contact sites, we conclude that this electrostatic component of interaction is insensitive to temperature and is not the determining factor differentiating the temperature sensitivity of ribosome assembly.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A computational investigation on the connection between dynamics properties of ribosomal proteins and ribosome assembly.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(5):e1002530. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002530. Epub 2012 May 24. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22654657 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity of ribosomal protein S8 from mesophilic and (hyper)thermophilic archaea and bacteria for 16S rRNA correlates with the growth temperatures of the organisms.FEBS Lett. 2003 Aug 14;549(1-3):123-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00760-9. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12914937
-
Molecular interactions within the halophilic, thermophilic, and mesophilic prokaryotic ribosomal complexes: clues to environmental adaptation.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2015;33(3):639-56. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2014.900457. Epub 2014 Apr 3. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2015. PMID: 24697502
-
Pseudouridines and pseudouridine synthases of the ribosome.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:147-59. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2001.66.147. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001. PMID: 12762017 Review.
-
Protein Assistants of Small Ribosomal Subunit Biogenesis in Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2022 Mar 30;10(4):747. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10040747. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35456798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Analysis Reveals Ancestral Lack of Seventeen Different tRNAs and Clade-Specific Loss of tRNA-CNNs in Archaea.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jun 7;9:1245. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01245. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29930548 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Human Genes Modulated by Porphyromonas gingivalis Highlights the Ribosome, Hypothalamus, and Cholinergic Neurons.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 14;12:646259. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.646259. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34194426 Free PMC article.
-
The nutritional composition and cell size of microbial biomass for food applications are defined by the growth conditions.Microb Cell Fact. 2023 Dec 11;22(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02265-1. Microb Cell Fact. 2023. PMID: 38072930 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral function of Inhibitors-of-kappaB regulates Caenorhabditis elegans development.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 30;10(1):16153. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73146-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32999373 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals New Insights Into the Common and Specific Metabolic Regulation of the Diatom Skeletonema dohrnii to the Silicate and Temperature Availability.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Nov 5;11:578915. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.578915. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33224167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Held WA, Ballou B, Mizushima S, Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30 S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. Further studies. Biol Chem. 1974;6:3103–3111. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

