Epitope mapping of inhibitory antibodies targeting the C2 domain of coagulation factor VIII by hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry
- PMID: 24152306
- PMCID: PMC3947443
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.12433
Epitope mapping of inhibitory antibodies targeting the C2 domain of coagulation factor VIII by hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry
Abstract
Background: The development of anti-factor VIII antibodies (inhibitors) is a significant complication in the management of patients with hemophilia A, leading to significant increases in morbidity and treatment cost. Using a panel of mAbs against different epitopes on FVIII, we have recently shown that epitope specificity, inhibitor kinetics and time to maximum inhibition are more important than inhibitor titer in predicting responses to FVIII and the combination of FVIII and recombinant FVIIa. In particular, a subset of high-titer inhibitors responded to high-dose FVIII, which would not be predicted on the basis of their inhibitor titer alone. Thus, the ability to quickly map the epitope spectrum of patient plasma with a clinically feasible assay may fundamentally change how clinicians approach the treatment of high-titer inhibitor patients.
Objectives: To map the epitopes of anti-FVIII mAbs, three of which are classic inhibitors and one of which is a non-classic inhibitor, by the use of hydrogen-deuterium exchange coupled with mass spectrometry (HDX-MS).
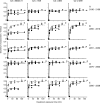
Methods: The binding epitopes of four mAbs targeting the FVIII C2 domain were mapped with HDX-MS.
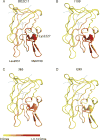
Results: The epitopes determined with HDX-MS are consistent with those obtained earlier through structural characterization and antibody competition assays. In addition, classic and non-classic inhibitor epitopes could be distinguished by the use of a limited subset of C2 domain-derived peptic fragments.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the HDX-MS method for epitope mapping, and suggest a potential role of rapid mapping of FVIII inhibitor epitopes in facilitating individualized treatment of inhibitor patients.
Keywords: antigen-antibody complex; epitope mapping; factor VIII; hemophilia A; hydrogen deuterium exchange measurement.
© 2013 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Scharrer I, Bray GL, Neutzling O. Incidence of inhibitors in haemophilia A patients--a review of recent studies of recombinant and plasma-derived factor VIII concentrates. Haemophilia. 1999;5:145–154. - PubMed
-
- Hoots WK. The future of plasma-derived clotting factor concentrates. Haemophilia. 2001;7(Suppl 1):4–9. - PubMed
-
- Bray GL, Gomperts ED, Courter S, Gruppo R, Gordon EM, Manco-Johnson M, Shapiro A, Scheibel E, White G, 3rd, Lee M. A multicenter study of recombinant factor VIII (recombinate): safety, efficacy, and inhibitor risk in previously untreated patients with hemophilia A. The Recombinate Study Group. Blood. 1994;83:2428–2435. - PubMed
-
- Lusher JM, Lee CA, Kessler CM, Bedrosian CL. The safety and efficacy of B-domain deleted recombinant factor VIII concentrate in patients with severe haemophilia A. Haemophilia. 2003;9:38–49. - PubMed
-
- Scandella D, Gilbert GE, Shima M, Nakai H, Eagleson C, Felch M, Prescott R, Rajalakshmi KJ, Hoyer LW, Saenko E. Some factor VIII inhibitor antibodies recognize a common epitope corresponding to C2 domain amino acids 2248 through 2312, which overlap a phospholipid-binding site. Blood. 1995;86:1811–1819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

