Aptamers as theranostic agents: modifications, serum stability and functionalisation
- PMID: 24152925
- PMCID: PMC3859083
- DOI: 10.3390/s131013624
Aptamers as theranostic agents: modifications, serum stability and functionalisation
Abstract
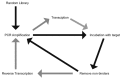
Aptamers, and the selection process known as Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX) used to generate them, were first described more than twenty years ago. Since then, there have been numerous modifications to the selection procedures. This review discusses the use of modified bases as a means of enhancing serum stability and producing effective therapeutic tools, as well as functionalising these nucleic acids to be used as potential diagnostic agents.
Figures


References
-
- Ellington A.D., Szostak J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990;346:818–822. - PubMed
-
- Robertson D.L., Joyce G.F. Selection in vitro of an RNA enzyme that specifically cleaves single-stranded DNA. Nature. 1990;344:467–468. - PubMed
-
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990;249:505–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

