Do knowledge brokers facilitate implementation of the stroke guideline in clinical practice?
- PMID: 24153114
- PMCID: PMC4015790
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6963-13-434
Do knowledge brokers facilitate implementation of the stroke guideline in clinical practice?
Abstract
Background: The implementation of clinical practice guidelines in rehabilitation practice is often troublesome and incomplete. An intervention to enhance the implementation of guidelines is the knowledge transfer program built around the activities of a knowledge broker (KB).This study investigates the use of KBs to implement guideline recommendations for intensive therapy and physical activity for patients post-stroke in 22 stroke units in hospitals and rehabilitation centers in The Netherlands.
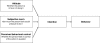
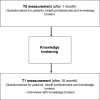
Methods/design: This study includes a quantitative evaluation with a non controlled pre-post intervention design and a mixed methods process evaluation. From each stroke unit, enterprising nurses and therapists will be recruited and trained as KB. The KB will work for one year on the implementation of the guideline recommendations in their team. To evaluate the effectiveness of the KB, a questionnaire will be administered to patients, health professionals and KBs at baseline (T0) and after one year (T1). Furthermore, semi structured interviews with 5 KBs will be performed at T1.The primary outcome of this implementation project will be the support health professionals give patients to exercise and be physically active, as reported by patients and health professionals themselves. The support immediately after the intervention is compared with the support at the start of the intervention.Additionally we will explore the influence of socio-demographic characteristics of health professionals and determinants identified in the Theory of Planned Behavior (intention, attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioral control) on the change of supportive behavior of health professionals. Finally, KBs will complete a questionnaire on their own psychological and social demographic characteristics and on organizational conditions needed for health-care improvement such as time, workforce, sponsoring and support from management.
Discussion: With this study we will gain insight in when and why knowledge brokers seem to be effective. Also we will identify determinants that predict which health professionals are susceptible to change their behavior. This study will provide guidance how to implement guidelines and will help to improve stroke rehabilitation services.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Encouraging post-stroke patients to be active seems possible: results of an intervention study with knowledge brokers.Disabil Rehabil. 2016 Aug;38(17):1748-55. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1107644. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Disabil Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 26763291
-
The impact of stroke practice guidelines on knowledge and practice patterns of acute care health professionals.J Eval Clin Pract. 2003 May;9(2):203-12. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2753.2003.00380.x. J Eval Clin Pract. 2003. PMID: 12787184
-
Physical therapists' guideline adherence on early mobilization and intensity of practice at dutch acute stroke units: a country-wide survey.Stroke. 2012 Sep;43(9):2395-401. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.660092. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Stroke. 2012. PMID: 22773556
-
Current use and barriers and facilitators for implementation of standardised measures in physical therapy in the Netherlands.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011 May 22;12:106. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-106. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011. PMID: 21600045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and effectiveness of knowledge brokers for translating clinical practice guidelines in health-related settings: a systematic review.BMJ Qual Saf. 2023 May;32(5):286-295. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2022-015595. Epub 2023 Feb 6. BMJ Qual Saf. 2023. PMID: 36746617
Cited by
-
Who does it first? The uptake of medical innovations in the performance of thrombolysis on ischemic stroke patients in Germany: a study based on hospital quality data.Implement Sci. 2015 Jan 13;10:10. doi: 10.1186/s13012-014-0196-7. Implement Sci. 2015. PMID: 25582164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaglehole R, Irwin A, Prentice T. The World Health Report 2003: Shaping the Future. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2003.
-
- Richtlijn ‘Diagnostiek, behandeling en zorg voor patiënten met een beroerte’. Utrecht: Nederlandse Vereniging voor Neurologie; 2008.
-
- Richtlijn ‘Beroerte’. Den Haag: Kwaliteitsinstituut voor de Gezondheidszorg CBO en Nederlandse Hartstichting; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical