Genetic and environmental determinants of human NK cell diversity revealed by mass cytometry
- PMID: 24154599
- PMCID: PMC3918221
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006702
Genetic and environmental determinants of human NK cell diversity revealed by mass cytometry
Abstract
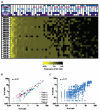
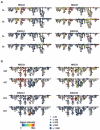
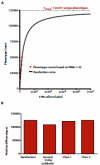
Natural killer (NK) cells play critical roles in immune defense and reproduction, yet remain the most poorly understood major lymphocyte population. Because their activation is controlled by a variety of combinatorially expressed activating and inhibitory receptors, NK cell diversity and function are closely linked. To provide an unprecedented understanding of NK cell repertoire diversity, we used mass cytometry to simultaneously analyze 37 parameters, including 28 NK cell receptors, on peripheral blood NK cells from 5 sets of monozygotic twins and 12 unrelated donors of defined human leukocyte antigen (HLA) and killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genotype. This analysis revealed a remarkable degree of NK cell diversity, with an estimated 6000 to 30,000 phenotypic populations within an individual and >100,000 phenotypes in the donor panel. Genetics largely determined inhibitory receptor expression, whereas activation receptor expression was heavily environmentally influenced. Therefore, NK cells may maintain self-tolerance through strictly regulated expression of inhibitory receptors while using adaptable expression patterns of activating and costimulatory receptors to respond to pathogens and tumors. These findings further suggest the possibility that discrete NK cell subpopulations could be harnessed for immunotherapeutic strategies in the settings of infection, reproduction, and transplantation.
Figures




Comment in
-
Natural killer cells: a virtual pick and mix.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Dec;13(12):844-5. doi: 10.1038/nri3566. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24189575 No abstract available.
-
Of snowflakes and natural killer cell subsets.Nat Biotechnol. 2014 Feb;32(2):140-2. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2810. Nat Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24509762 No abstract available.
-
21st century natural killers.Nat Rev Immunol. 2019 Feb;19(2):69. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0120-0. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30626905 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kiessling R, Klein E, Wigzell H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur. J. Immunol. 1975;5:112–117. - PubMed
-
- Kiessling R, Klein E, Wigzell H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur. J. Immunol. 1975;5:112–117. - PubMed
-
- Herberman RR, Ortaldo JR, Bonnard GD. Augmentation by interferon of human natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1979;277:221–223. - PubMed
-
- Ortaldo JR, Bonnard GD, Kind PD, Herberman RB. Cytotoxicity by cultured human lymphocytes: characteristics of effector cells and specificity of cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1979;122:1489–1494. - PubMed
-
- Biron CA, Welsh RM. Activation and role of natural killer cells in virus infections. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1982;170:155–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007290/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI07290/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI22039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA011170/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI090019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI022039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001085/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DA011170/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- ES022153/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA023063/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES022153/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI090019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA111412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI090019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DA023063/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

