Cholesterol as a co-solvent and a ligand for membrane proteins
- PMID: 24155031
- PMCID: PMC3892294
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2385
Cholesterol as a co-solvent and a ligand for membrane proteins
Abstract
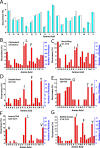
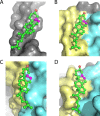
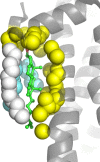
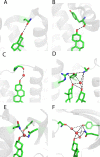
As of mid 2013 a Medline search on "cholesterol" yielded over 200,000 hits, reflecting the prominence of this lipid in numerous aspects of animal cell biology and physiology under conditions of health and disease. Aberrations in cholesterol homeostasis underlie both a number of rare genetic disorders and contribute to common sporadic and complex disorders including heart disease, stroke, type II diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease. The corresponding author of this review and his lab stumbled only recently into the sprawling area of cholesterol research when they discovered that the amyloid precursor protein (APP) binds cholesterol, a topic covered by the Hans Neurath Award lecture at the 2013 Protein Society Meeting. Here, we first provide a brief overview of cholesterol-protein interactions and then offer our perspective on how and why binding of cholesterol to APP and its C99 domain (β-CTF) promotes the amyloidogenic pathway, which is closely related to the etiology of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; C99; CRAC; GPCRs; amyloid precursor protein; cholesterol; integral membrane proteins; receptor; β-CTF.
© 2013 The Protein Society.
Figures
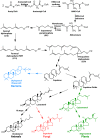
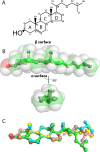

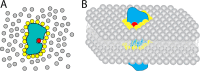
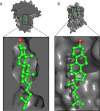
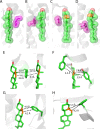
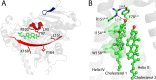
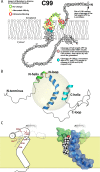
References
-
- Zambrano F, Fleischer S, Fleischer B. Lipid composition of the Golgi apparatus of rat kidney and liver in comparison with other subcellular organelles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975;380:357–369. - PubMed
-
- Andreyev AY, Fahy E, Guan Z, Kelly S, Li X, McDonald JG, Milne S, Myers D, Park H, Ryan A, Thompson BM, Wang E, Zhao Y, Brown HA, Merrill AH, Raetz CR, Russell DW, Subramaniam S, Dennis EA. Subcellular organelle lipidomics in TLR-4-activated macrophages. J Lipid Res. 2010;51:2785–2797. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wood WG, Cornwell M, Williamson LS. High performance thin-layer chromatography and densitometry of synaptic plasma membrane lipids. J Lipid Res. 1989;30:775–779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

