Alpha 2B adrenoceptor genotype moderates effect of reboxetine on negative emotional memory bias in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 24155306
- PMCID: PMC6618435
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2124-13.2013
Alpha 2B adrenoceptor genotype moderates effect of reboxetine on negative emotional memory bias in healthy volunteers
Abstract
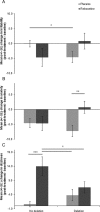
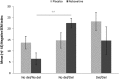
Evidence suggests that emotional memory plays a role in the pathophysiology of depression/anxiety disorders. Noradrenaline crucially modulates emotional memory. Genetic variants involved in noradrenergic signaling contribute to individual differences in emotional memory and vulnerability to psychopathology. A functional deletion polymorphism in the α-2B adrenoceptor gene (ADRA2B) has been linked to emotional memory and post-traumatic stress disorder. The noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor reboxetine attenuates enhanced memory for negative stimuli in healthy and depressed individuals. We examined whether the effect of reboxetine on emotional memory in healthy individuals would be moderated by ADRA2B genotype. ADRA2B deletion carriers demonstrated enhanced emotional memory for negative stimuli compared with deletion noncarriers, consistent with prior studies. Reboxetine attenuated enhanced memory for negative stimuli in deletion noncarriers but had no significant effect in deletion carriers. This is the first demonstration of genetic variation influencing antidepressant drug effects on emotional processing in healthy humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Catechol-O-methyltransferase val158met genotype determines effect of reboxetine on emotional memory in healthy male volunteers.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2014 May;39(3):E24-31. doi: 10.1503/jpn.130131. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24467942 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Deletion Variant of the α2b-Adrenoceptor Modulates the Stress-Induced Shift from "Cognitive" to "Habit" Memory.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 22;37(8):2149-2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3507-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jan 23. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28115477 Free PMC article.
-
ADRA2B genotype differentially modulates stress-induced neural activity in the amygdala and hippocampus during emotional memory retrieval.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Feb;232(4):755-64. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3710-3. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25127926
-
ADRA2B deletion variant and enhanced cognitive processing of emotional information: A meta-analytical review.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018 Sep;92:402-416. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.05.010. Epub 2018 May 8. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018. PMID: 29751052 Review.
-
The need for new and better antidepressants: reboxetine a new option.Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000;402:6-11. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.02602.x. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000. PMID: 10901153 Review.
Cited by
-
A neurocognitive model for understanding treatment action in depression.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Sep 19;370(1677):20140213. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0213. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26240428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The power of negative and positive episodic memories.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2022 Oct;22(5):869-903. doi: 10.3758/s13415-022-01013-z. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35701665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of sertraline on emotional processing: secondary analyses of the PANDA randomised controlled trial.Psychol Med. 2022 Oct;52(13):2814-2821. doi: 10.1017/S0033291720004985. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Psychol Med. 2022. PMID: 33431087 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adrenoceptors: A Focus on Psychiatric Disorders and Their Treatments.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;285:507-554. doi: 10.1007/164_2023_675. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37495853 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
