Minimal features of efficient incorporation of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein into sendai virus particles
- PMID: 24155372
- PMCID: PMC3911711
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02041-13
Minimal features of efficient incorporation of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein into sendai virus particles
Abstract
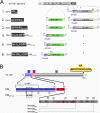
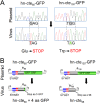
Two transmembrane glycoproteins form spikes on the surface of Sendai virus, a member of the Respirovirus genus of the Paramyxovirinae subfamily of the Paramyxoviridae family: the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) and the fusion (F) proteins. HN, in contrast to F, is dispensable for viral particle production, as normal amounts of particles can be produced with highly reduced levels of HN. This HN reduction can result from mutation of an SYWST motif in its cytoplasmic tail to AFYKD. HNAFYKD accumulates at the infected cell surface but does not get incorporated into particles. In this work, we derived experimental tools to rescue HNAFYKD incorporation. We found that coexpression of a truncated HN harboring the wild-type cytoplasmic tail, the transmembrane domain, and at most 80 amino acids of the ectodomain was sufficient to complement defective HNAFYKD incorporation into particles. This relied on formation of disulfide-bound heterodimers carried out by the two cysteines present in the HN 80-amino-acid (aa) ectodomain. Finally, the replacement of the measles virus H cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains with the corresponding HN domains promoted measles virus H incorporation in Sendai virus particles.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sendai virus particle production: basic requirements and role of the SYWST motif present in HN cytoplasmic tail.Virology. 2010 Sep 30;405(2):439-47. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.06.030. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Virology. 2010. PMID: 20633915
-
Peptides derived from the heptad repeat region near the C-terminal of Sendai virus F protein bind the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase ectodomain.FEBS Lett. 2003 Feb 11;536(1-3):56-60. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00010-3. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12586338
-
Structure-function analysis of the Sendai virus F and HN cytoplasmic domain: different role for the two proteins in the production of virus particle.Virology. 2000 May 10;270(2):464-75. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0291. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10793005
-
Cytoplasmic domain of Sendai virus HN protein contains a specific sequence required for its incorporation into virions.J Virol. 1998 Dec;72(12):9747-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.12.9747-9754.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9811709 Free PMC article.
-
Paramyxovirus membrane fusion: lessons from the F and HN atomic structures.Virology. 2006 Jan 5;344(1):30-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.09.007. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16364733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered cell function and increased replication of rhinoviruses and EV-D68 in airway epithelia of asthma patients.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 1;14:1106945. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1106945. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36937308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lamb RA, Parks GD. 2007. Paramyxoviridae: the viruses and their replication, p 1449–1496 In Knipe DM, Howley PM. (ed), Fields virology, 5th ed, vol 1 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
-
- Bose S, Welch BD, Kors CA, Yuan P, Jardetzky TS, Lamb RA. 2011. Structure and mutagenesis of the parainfluenza virus 5 hemagglutinin-neuraminidase stalk domain reveals a four-helix bundle and the role of the stalk in fusion promotion. J. Virol. 85:12855–12866. 10.1128/JVI.06350-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

