Latent gammaherpesvirus 68 infection induces distinct transcriptional changes in different organs
- PMID: 24155394
- PMCID: PMC3911696
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02708-13
Latent gammaherpesvirus 68 infection induces distinct transcriptional changes in different organs
Abstract
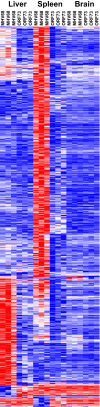
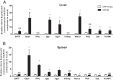
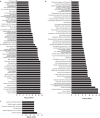
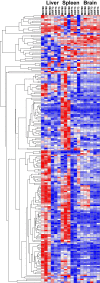
Previous studies identified a role for latent herpesvirus infection in cross-protection against infection and exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases. Here, we identified more than 500 genes differentially expressed in spleens, livers, or brains of mice latently infected with gammaherpesvirus 68 and found that distinct sets of genes linked to different pathways were altered in the spleen compared to those in the liver. Several of the most differentially expressed latency-specific genes (e.g., the gamma interferon [IFN-γ], Cxcl9, and Ccl5 genes) are associated with known latency-specific phenotypes. Chronic herpesvirus infection, therefore, significantly alters the transcriptional status of host organs. We speculate that such changes may influence host physiology, the status of the immune system, and disease susceptibility.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamma interferon blocks gammaherpesvirus reactivation from latency.J Virol. 2006 Jan;80(1):192-200. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.1.192-200.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16352543 Free PMC article.
-
Immune control of the number and reactivation phenotype of cells latently infected with a gammaherpesvirus.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(14):7125-32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.14.7125-7132.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12072512 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma interferon blocks gammaherpesvirus reactivation from latency in a cell type-specific manner.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):6134-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00108-07. Epub 2007 Mar 14. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17360749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LXR Alpha Restricts Gammaherpesvirus Reactivation from Latently Infected Peritoneal Cells.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e02071-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02071-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30602604 Free PMC article.
-
Natural history of murine gamma-herpesvirus infection.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001 Apr 29;356(1408):569-79. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0779. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001. PMID: 11313012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drawing on disorder: How viruses use histone mimicry to their advantage.J Exp Med. 2018 Jul 2;215(7):1777-1787. doi: 10.1084/jem.20180099. Epub 2018 Jun 22. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29934321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsic p53 activation restricts gammaherpesvirus driven germinal center B cell expansion during latency establishment.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 22;16(1):951. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56247-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39843898 Free PMC article.
-
What do animal models tell us about the role of EBV in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis?Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1036155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1036155. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metagenomic analysis of intestinal mucosa revealed a specific eukaryotic gut virome signature in early-diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease.Gut Microbes. 2019;10(2):149-158. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2018.1511664. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Gut Microbes. 2019. PMID: 30252582 Free PMC article.
-
Unmasking the tissue-resident eukaryotic DNA virome in humans.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Apr 24;51(7):3223-3239. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad199. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36951096 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

