Articaine for surgical removal of impacted third molar; a comparison with lignocaine
- PMID: 24155578
- PMCID: PMC3768079
Articaine for surgical removal of impacted third molar; a comparison with lignocaine
Abstract
Aim: Articaine is an amide local anesthetic that differs from other agents of its group due to the presence of thiophene ring instead of a benzene ring. Some researchers claim that articaine is superior to lidocaine in its biologic profile. The aim of the study is to compare the efficacy of articaine with that of lidocaine which has proven efficacy.
Materials and method: This study was done on 50 subjects; 25 of them received 4 % articaine HCl with 1:100000 epinephrine and the next 25 received 2% lignocaine HCl with 1:100000 epinephrine. Time of injection, onset of anesthesia, amount of anesthetic injected were recorded. Efficacy was determined using visual analog scale. The values were statistically analyzed.
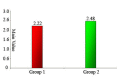
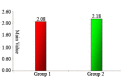
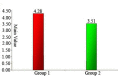
Results: The mean onset time of anesthesia in study group was 2.07 ± 0.22 and 2.18 ± 0.26 minutes in comparison group. A mean duration of 4.28 +0.78 hours was seen with articaine group and 3.51 + 0.45 hours with the lignocaine group. No statistical difference between the two groups with regard to pain experience.
Conclusion: Articaine has similar efficacy as that of lignocaine with slightly longer duration and can be used as an alternative to lignocaine in third molar surgeries.
Clinical significance: Increased availability of local anesthetics has improved interest in research about dental pain control. a quest for new methods of pain reduction is always justified. How to cite this article: R Shruthi, S N Kedarnath, S Mamatha N, Rajaram P, Dinesh B. Articaine For Surgical Removal of Impacted Third Molar; A Comparison With Lignocaine. J Int Oral Health 2013; 5(1):48-53.
Keywords: Local anaesthesia; articaine; efficacy; lignocaine; visual analogue scale.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None Declared
Figures
References
-
- Malamed SF. Handbook of local anesthesia. 5. St Louis; Mosby: 2004. p. 5.
-
- Costa CG, Tortamano IP, Rocha RG, Francischone CE. Onset and duration periods of articaine and lidocaine on maxillary infiltration. Quintessence Int. 2005;36:197–201. - PubMed
-
- Vree TB, Gielen MJ. Clinical pharmacology and the use of articaine for local and regional anaesthesia. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2005;19(2):293–308. - PubMed
-
- Chaffey E, Reader A, Nusstein J, Beck M, Weaver J. Anesthetic efficacy of articaine for inferior alveolar nerve blocks in patients with irreversible pulpitis. J Endod. 2004;30(8):568–571. - PubMed
-
- Malamed SF, Gagnon S, Leblanc D. Efficacy of articaine: a new amide local anesthetic. J Am Dent Assoc. 2000;131(5):635–642. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources