The many faces of C/EBPδ and their relevance for inflammation and cancer
- PMID: 24155666
- PMCID: PMC3805898
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.7224
The many faces of C/EBPδ and their relevance for inflammation and cancer
Abstract
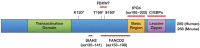
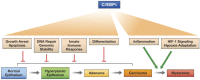
The CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (CEBPD, C/EBPδ) is a transcription factor that modulates many biological processes including cell differentiation, motility, growth arrest, proliferation, and cell death. The diversity of C/EBPδ's functions depends in part on the cell type and cellular context and can have opposing outcomes. For example, C/EBPδ promotes inflammatory signaling, but it can also inhibit pro-inflammatory pathways, and in a mouse model of mammary tumorigenesis, C/EBPδ reduces tumor incidence but promotes tumor metastasis. This review highlights the multifaceted nature of C/EBPδ's functions, with an emphasis on pathways that are relevant for cancer and inflammation, and illustrates how C/EBPδ emerged from the shadow of its family members as a fascinating "jack of all trades." Our current knowledge on C/EBPδ indicates that, rather than being essential for a specific cellular process, C/EBPδ helps to interpret a variety of cues in a cell-type and context-dependent manner, to adjust cellular functions to specific situations. Therefore, insights into the roles and mechanisms of C/EBPδ signaling can lead to a better understanding of how the integration of different signaling pathways dictates normal and pathological cell functions and physiology.
Keywords: C/EBP; cancer.; cell signaling; inflammation; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Tsukada J, Yoshida Y, Kominato Y, Auron PE. The CCAAT/enhancer (C/EBP) family of basic-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors is a multifaceted highly-regulated system for gene regulation. Cytokine. 2011;54:6–19. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2010.12.019. - PubMed
-
- Nerlov C. The C/EBP family of transcription factors: a paradigm for interaction between gene expression and proliferation control. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:318–24. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2007.07.004. - PubMed
-
- Sebastian T, Johnson PF. Stop and go: anti-proliferative and mitogenic functions of the transcription factor C/EBPbeta. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:953–7. - PubMed
-
- Roos AB, Nord M. The emerging role of C/EBPs in glucocorticoid signaling: lessons from the lung. J Endocrinol. 2012;212:291–305. doi:10.1530/JOE-11-0369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

