Glutamate, glutamate receptors, and downstream signaling pathways
- PMID: 24155668
- PMCID: PMC3805900
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.6426
Glutamate, glutamate receptors, and downstream signaling pathways
Abstract
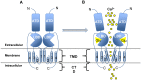
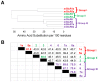
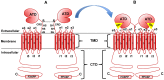
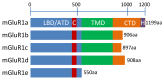
Glutamate is a nonessential amino acid, a major bioenergetic substrate for proliferating normal and neoplastic cells, and an excitatory neurotransmitter that is actively involved in biosynthetic, bioenergetic, metabolic, and oncogenic signaling pathways. Glutamate signaling activates a family of receptors consisting of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) and ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs), both of which have been implicated in chronic disabling brain disorders such as Schizophrenia and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and multiple sclerosis. In this review, we discuss the structural and functional relationship of mGluRs and iGluRs and their downstream signaling pathways. The three groups of mGluRs, the associated second messenger systems, and subsequent activation of PI3K/Akt, MAPK, NFkB, PLC, and Ca/CaM signaling systems will be discussed in detail. The current state of human mGluR1a as one of the most important isoforms of Group I-mGluRs will be highlighted. The lack of studies on the human orthologues of mGluRs family will be outlined. We conclude that upon further study, human glutamate-initiated signaling pathways may provide novel therapeutic opportunities for a variety of non-malignant and malignant human diseases.
Keywords: GRM1a; Glutamate; iGluR; mGluR; signaling..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

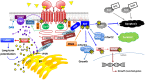
Similar articles
-
Glutamate and its receptors in cancer.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Aug;121(8):933-44. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1182-6. Epub 2014 Mar 9. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014. PMID: 24610491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamate signaling in benign and malignant disorders: current status, future perspectives, and therapeutic implications.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Aug 9;9(7):728-42. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6475. eCollection 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23983606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Costimulation of AMPA and metabotropic glutamate receptors underlies phospholipase C activation by glutamate in hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2015 Apr 22;35(16):6401-12. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4208-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25904792 Free PMC article.
-
[Excitatory amino acid receptors].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1994 Sep;104(3):177-87. doi: 10.1254/fpj.104.177. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1994. PMID: 7959410 Review. Japanese.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors and neurodegenerative diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jan;115:179-191. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.013. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 27872019 Review.
Cited by
-
NMDA Receptors: Distribution, Role, and Insights into Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;17(10):1265. doi: 10.3390/ph17101265. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo glucose metabolism and glutamate levels in mGluR5 knockout mice: a multimodal neuroimaging study using [18F]FDG microPET and MRS.EJNMMI Res. 2020 Oct 2;10(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s13550-020-00716-z. EJNMMI Res. 2020. PMID: 33006705 Free PMC article.
-
Role of glutamate excitotoxicity and glutamate transporter EAAT2 in epilepsy: Opportunities for novel therapeutics development.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Nov;193:114786. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114786. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34571003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Glutamate Receptors in Epilepsy.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 4;11(3):783. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030783. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroregulatory role of ginkgolides.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jul;48(7):5689-5697. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06535-2. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34245409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kelly A, Stanley CA. Disorders of glutamate metabolism. Mental retardation and developmental disabilities research reviews. 2001;7:287–95. - PubMed
-
- Alix JJ, Domingues AM. White matter synapses: form, function, and dysfunction. Neurology. 2011;76:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Fairman WA, Amara SG. Functional diversity of excitatory amino acid transporters: ion channel and transport modes. The American journal of physiology. 1999;277:F481–6. - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro FM, Paquet M, Cregan SP, Ferguson SS. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor signalling and its implication in neurological disease. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets. 2010;9:574–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

