Molecular characterization and alternative splicing of a sodium channel and DSC1 ortholog genes in Liposcelis bostrychophila Badonnel (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae)
- PMID: 24155671
- PMCID: PMC3805903
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.6978
Molecular characterization and alternative splicing of a sodium channel and DSC1 ortholog genes in Liposcelis bostrychophila Badonnel (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae)
Abstract
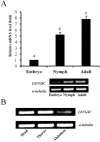
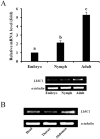
Alternative splicing greatly contributes to the structural and functional diversity of voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) by generating various isoforms with unique functional and pharmacological properties. Here, we identified a new optional exon 23 located in the linker between domains II and III, and four mutually exclusive exons (exons 27A, 27B, 27C, and 27D) in domains IIIS3 and IIIS4 of the sodium channel of Liposcelis bostrychophila (termed as LbVGSC). This suggested that more alternative splicing phenomena remained to be discovered in VGSCs. Inclusion of exon 27C might lead to generation of non-functional isoforms. Meanwhile, identification of three alternative exons (exons 11, 13A, and 13B), which were located in the linker between domains II and III, indicated that abundant splicing events occurred in the DSC1 ortholog channel of L. bostrychophila (termed as LbSC1). Exons 13A and 13B were generated by intron retention, and the presence of exon 13B relied on the inclusion of exon 13A. Exon 13B was specifically expressed in the embryonic stage and contained an in-frame stop codon, inclusion of which led to generation of truncated proteins with only the first two domains. Additionally, several co-occurring RNA editing events were identified in LbSC1. Furthermore, remarkable similarity between the structure and expression patterns of LbVGSC and LbSC1 were discovered, and a closer evolutionary relationship between VGSCs and DSC1 orthologs was verified. Taken together, the data provided abundant molecular information on VGSC and DSC1 orthologs in L. bostrychophila, a representative Psocoptera storage pest, and insights into the alternative splicing of these two channels.
Keywords: Alternative splicing; DSC1; Liposcelis bostrychophila; RNA editing.; VGSC; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Distinct functional properties of sodium channel variants are associated with usage of alternative exons in Nilaparvata lugens.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Mar;118:103292. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2019.103292. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31811885 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an insect heterodimeric voltage-gated sodium channel with unique alternative splicing mode.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Jan;203:149-158. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27816572
-
Molecular characterization and functional expression of the DSC1 channel.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Jul;41(7):451-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.04.010. Epub 2011 May 7. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21571069 Free PMC article.
-
Functional diversity in neuronal voltage-gated calcium channels by alternative splicing of Ca(v)alpha1.Mol Neurobiol. 2002 Aug;26(1):21-44. doi: 10.1385/MN:26:1:021. Mol Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 12392054 Review.
-
Alternative splicing and insect ryanodine receptor.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019 Nov;102(3):e21590. doi: 10.1002/arch.21590. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31218747 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct functional properties of sodium channel variants are associated with usage of alternative exons in Nilaparvata lugens.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Mar;118:103292. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2019.103292. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31811885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Catterall WA. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: The structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000;26:13–25. - PubMed
-
- Salkoff L, Butler A, Wei A. et al. Genomic organization and deduced amino acid sequence of a putative sodium channel gene in Drosophila. Sci. 1987;237:744–749. - PubMed
-
- Loughney K, Kreber R, Ganetzky B. Molecular analysis of the para locus, a sodium-channel gene in Drosophila. Cell. 1989;58:1143–1154. - PubMed
-
- Littleton JT, Ganetzky B. Ion channels and synaptic viewpoint organization: analysis of the Drosophila genome. Neuron. 2000;26:35–43. - PubMed
-
- Liu ZQ, Chung I, Dong K. Alternative splicing of the BSC1 gene generates tissue-specific isoforms in the German cockroach. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2001;31:703–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

