Imaging neuron-glia interactions in the enteric nervous system
- PMID: 24155689
- PMCID: PMC3801083
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00183
Imaging neuron-glia interactions in the enteric nervous system
Abstract
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a network of neurons and glia within the wall of the gastrointestinal tract that is able to control many aspects of digestive function independently from the central nervous system. Enteric glial cells share several features with astrocytes and are closely associated with enteric neurons and their processes both within enteric ganglia, and along interconnecting fiber bundles. Similar to other parts of the nervous system, there is communication between enteric neurons and glia; enteric glial cells can detect neuronal activity and have the machinery to intermediate neurotransmission. However, due to the close contact between these two cell types and the particular characteristics of the gut wall, the recording of enteric glial cell activity in live imaging experiments, especially in the context of their interaction with neurons, is not straightforward. Most studies have used calcium imaging approaches to examine enteric glial cell activity but in many cases, it is difficult to distinguish whether observed transients arise from glial cells, or neuronal processes or varicosities in their vicinity. In this technical report, we describe a number of approaches to unravel the complex neuron-glia crosstalk in the ENS, focusing on the challenges and possibilities of live microscopic imaging in both animal models and human tissue samples.
Keywords: GCaMP; calcium; enteric glia; enteric neuron; synaptic.
Figures
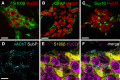
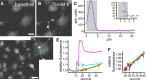
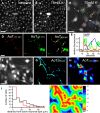
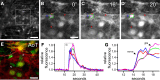
Similar articles
-
Structurally defined signaling in neuro-glia units in the enteric nervous system.Glia. 2019 Jun;67(6):1167-1178. doi: 10.1002/glia.23596. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Glia. 2019. PMID: 30730592 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic neuron-to-glia signaling in the enteric nervous system.Gastroenterology. 2009 Apr;136(4):1349-58. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.058. Epub 2009 Jan 1. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19250649
-
Neurons, Macrophages, and Glia: The Role of Intercellular Communication in the Enteric Nervous System.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1383:251-258. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-05843-1_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36587164 Review.
-
Cholinergic activation of enteric glia is a physiological mechanism that contributes to the regulation of gastrointestinal motility.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):G473-G483. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00155.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29927320 Free PMC article.
-
The enteric glia: identity and functions.Glia. 2015 Jun;63(6):921-35. doi: 10.1002/glia.22795. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Glia. 2015. PMID: 25703790 Review.
Cited by
-
β-adrenergic signaling triggers enteric glial reactivity and acute enteric gliosis during surgery.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Nov 8;20(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02937-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37941007 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Tools to Investigate Cellular Activity in the Intestinal Wall.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015 Jul 30;21(3):337-51. doi: 10.5056/jnm15096. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. PMID: 26130630 Free PMC article.
-
Unique Neural Circuit Connectivity of Mouse Proximal, Middle, and Distal Colon Defines Regional Colonic Motor Patterns.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;13(1):309-337.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.08.016. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34509687 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic integration of enteric neural stem cells in ex vivo organotypic colon cultures.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 5;11(1):15889. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95434-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34354183 Free PMC article.
-
The New Calcium Imaging Trend (Front Cell Neurosci 2015;9:436).J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Apr 30;22(2):346-7. doi: 10.5056/jnm15197. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016. PMID: 26876959 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bisschops R., Vanden Berghe P., Sarnelli G., Janssens J., Tack J. (2006). CRF-induced calcium signaling in guinea pig small intestine myenteric neurons involves CRF-1 receptors and activation of voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Am J Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 290, G1252–G1260 10.1152/ajpgi.00349.2004 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

