The analgesic effect of nefopam with fentanyl at the end of laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- PMID: 24156002
- PMCID: PMC3800708
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.361
The analgesic effect of nefopam with fentanyl at the end of laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Abstract
Background: Nefopam is a centrally acting analgesic that is used to control pain. The aim of this study was to find an appropriate dose of nefopam that demonstrates an analgesic effect when administered in continuous infusion with fentanyl at the end of laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
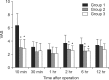
Methods: Ninety patients scheduled for laparoscopic cholecystectomy were randomly assigned to receive analgesia with fentanyl alone (50 µg, Group 1, n = 30), or with fentanyl in combination with nefopam 20 mg (Group 2, n = 30) or in combination with nefopam 40 mg (Group 3, n = 30) at the end of surgery. Pain and side effects were evaluated at 10 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, 6 hours, and 12 hours after arrival in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU).
Results: Pain was statistically significantly lower in Groups 2 and 3 than in Group 1 at 10 minutes, 2 hours, and 6 hours after arrival in the PACU. Nausea was statistically significantly lower in Group 2 than in Groups 1 and 3 at 10 minutes after arrival in the PACU. Shivering was statistically significantly lower in Groups 2 and 3 than in Group 1 at 10 minutes after arrival in the PACU.
Conclusions: Nefopam is a drug that can be safely used as an analgesic after surgery, and its side effects can be reduced when fentanyl 50 µg is injected with nefopam 20 mg.
Keywords: fentanyl; laparoscopic cholecystectomy; nefopam; pain.
Figures
References
-
- Klohs MW, Draper MD, Petracek FJ, Ginzel KH, Ré ON. Benzoxazocines: a new chemical class of centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxants. Arzneimittelforschung. 1972;22:132–133. - PubMed
-
- Gassel MM, Diamantopoulos E, Petropoulos V, Hughes AC, Ballesteros ML, Ré ON. Controlled clinical trial of oral and parenteral nefopam hydrochloride. A novel and potent analgesic drug. J Clin Pharmacol. 1976;16:34–41. - PubMed
-
- Piercey MF, Schroeder LA. Spinal and supraspinal sites for morphine and nefopam analgesia in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981;74:135–140. - PubMed
-
- Kehlet H, Dahl JB. The value of "multimodal" or "balanced analgesia" in postoperative pain treatment. Anesth Analg. 1993;77:1048–1056. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources