Robotic versus Laparoscopic versus Open Gastrectomy: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 24156033
- PMCID: PMC3804672
- DOI: 10.5230/jgc.2013.13.3.136
Robotic versus Laparoscopic versus Open Gastrectomy: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To define the role of robotic gastrectomy for the treatment of gastric cancer, the present systematic review with meta-analysis was performed.
Materials and methods: A comprehensive search up to July 2012 was conducted on PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library. All eligible studies comparing robotic gastrectomy versus laparoscopic gastrectomy or open gastrectomy were included.
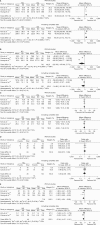
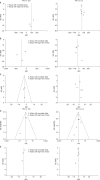
Results: Included in our meta-analysis were seven studies of 1,967 patients that compared robotic (n=404) with open (n=718) or laparoscopic (n=845) gastrectomy. In the complete analysis, a shorter hospital stay was noted with robotic gastrectomy than with open gastrectomy (weighted mean difference: -2.92, 95% confidence interval: -4.94 to -0.89, P=0.005). Additionally, there was a significant reduction in intraoperative blood loss with robotic gastrectomy compared with laparoscopic gastrectomy (weighted mean difference: -35.53, 95% confidence interval: -66.98 to -4.09, P=0.03). These advantages were at the price of a significantly prolonged operative time for both robotic gastrectomy versus laparoscopic gastrectomy (weighted mean difference: 63.70, 95% confidence interval: 44.22 to 83.17, P<0.00001) and robotic gastrectomy versus open gastrectomy (weighted mean difference: 95.83, 95% confidence interval: 54.48 to 137.18, P<0.00001). Analysis of the number of lymph nodes retrieved and overall complication rates revealed that these outcomes did not differ significantly between the groups.
Conclusions: Robotic gastrectomy for gastric cancer reduces intraoperative blood loss and the postoperative hospital length of stay compared with laparoscopic gastrectomy and open gastrectomy at a cost of a longer operating time. Robotic gastrectomy also provides an oncologically adequate lymphadenectomy. Additional high-quality prospective studies are recommended to better evaluate both short and long-term outcomes.
Keywords: Gastrectomy; Laparoscopy; Robotics; Stomach neoplasms.
Figures


References
-
- Kitano S, Shiraishi N. Minimally invasive surgery for gastric tumors. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:151–164. - PubMed
-
- Kitano S, Iso Y, Moriyama M, Sugimachi K. Laparoscopy-assisted Billroth I gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1994;4:146–148. - PubMed
-
- Kim HH, Hyung WJ, Cho GS, Kim MC, Han SU, Kim W, et al. Morbidity and mortality of laparoscopic gastrectomy versus open gastrectomy for gastric cancer: an interim report--a phase III multicenter, prospective, randomized Trial (KLASS Trial) Ann Surg. 2010;251:417–420. - PubMed
-
- Kim YW, Baik YH, Yun YH, Nam BH, Kim DH, Choi IJ, et al. Improved quality of life outcomes after laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy for early gastric cancer: results of a prospective randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg. 2008;248:721–727. - PubMed
-
- Katai H, Sasako M, Fukuda H, Nakamura K, Hiki N, Saka M, et al. JCOG Gastric Cancer Surgical Study Group. Safety and feasibility of laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy with suprapancreatic nodal dissection for clinical stage I gastric cancer: a multicenter phase II trial (JCOG 0703) Gastric Cancer. 2010;13:238–244. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

