Endothelial Krüppel-like factor 4 modulates pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 24156273
- PMCID: PMC4068930
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0135OC
Endothelial Krüppel-like factor 4 modulates pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
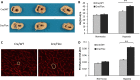
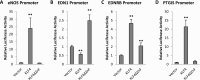
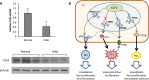
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a transcription factor expressed in the vascular endothelium, where it promotes anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant states, and increases endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression. We examined the role of endothelial KLF4 in pulmonary arterial (PA) hypertension (PAH). Mice with endothelial KLF4 knockdown were exposed to hypoxia for 3 weeks, followed by measurement of right ventricular and PA pressures, pulmonary vascular muscularization, and right ventricular hypertrophy. The effect of KLF4 on target gene expression was assessed in lungs from these mice, verified in vitro by small interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown of KLF4, and further studied at the promoter level with cotransfection experiments. KLF4 expression was measured in lung tissue from patients with PAH and normal control subjects. We found that, after hypoxia, right ventricular and PA pressures were significantly higher in KLF4 knockdown animals than controls. Knockdown animals also had more severe pulmonary vascular muscularization and right ventricular hypertrophy. KLF4 knockdown resulted in increased pulmonary expression of endothelin-1 and decreased expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, endothelin receptor subtype B, and prostacyclin synthase. Concordant findings were observed in vitro, both with siRNA knockdown of KLF4 and promoter activity assays. Finally, KLF4 expression was reduced in lungs from patients with PAH. In conclusion, endothelial KLF4 regulates the transcription of genes involved in key pathways implicated in PAH, and its loss exacerbates pulmonary hypertension in response to chronic hypoxia in mice. These results introduce a novel transcriptional modulator of PAH, with the potential of becoming a new therapeutic target.
Figures


References
-
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH, Rosenson RS, et al. American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents; American Heart Association; American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; Pulmonary Hypertension Association. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:1573–1619. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, Morrell NW, Archer SL, Stenmark KR, MacLean MR, Lang IM, Christman BW, Weir EK, Eickelberg O, Voelkel NF, et al. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(12 Suppl S):13S–24S. - PubMed
-
- Dorfmüller P, Perros F, Balabanian K, Humbert M. Inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2003;22:358–363. - PubMed
-
- Farber HW, Loscalzo J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1655–1665. - PubMed
-
- Atkins GB, Jain MK. Role of Krüppel-like transcription factors in endothelial biology. Circ Res. 2007;100:1686–1695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08HL083090/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086548/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097593/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110630/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL086548/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL1124861/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL083090/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113570/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL110630/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076754/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL097593/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL076754/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

