Molecular docking studies for the identification of novel melatoninergic inhibitors for acetylserotonin-O-methyltransferase using different docking routines
- PMID: 24156411
- PMCID: PMC3819668
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4682-10-63
Molecular docking studies for the identification of novel melatoninergic inhibitors for acetylserotonin-O-methyltransferase using different docking routines
Abstract
Background: N-Acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase (ASMT) is an enzyme which by converting nor-melatonin to melatonin catalyzes the final reaction in melatonin biosynthesis in tryptophan metabolism pathway. High Expression of ASMT gene is evident in PPTs. The presence of abnormally high levels of ASMT in pineal gland could serve as an indication of the existence of pineal parenchymal tumors (PPTs) in the brain (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65: 675-684, 2006). Different levels of melatonin are used as a trait marker for prescribing the mood disorders e.g. Seasonal affective disorder, bipolar disorder, or major depressive disorder. In addition, melatonin levels can also be used to calculate the severity of a patient's illness at a given point in time.
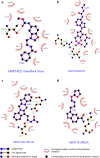
Methods: Seventy three melatoninergic inhibitors were docked with acetylserotonin-O-methyltransferase in order to identify the potent inhibitor against the enzyme. The chemical nature of the protein and ligands greatly influence the performance of docking routines. Keeping this fact in view, critical evaluation of the performance of four different commonly used docking routines: AutoDock/Vina, GOLD, FlexX and FRED were performed. An evaluation criterion was based on the binding affinities/docking scores and experimental bioactivities.
Results and conclusion: Results indicated that both hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions contributed significantly for its ligand binding and the compound selected as potent inhibitor is having minimum binding affinity, maximum GoldScore and minimum FlexX energy. The correlation value of r2 = 0. 66 may be useful in the selection of correct docked complexes based on the energy without having prior knowledge of the active site. This may lead to further understanding of structures, their reliability and Biomolecular activity especially in connection with bipolar disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Donohue SJ, Roseboom PH, Illnerova H, Weller JL, Klein DC. Human hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase: presence of LINE-1 fragment in a cDNA clone and pineal mRNA. DNA Cell Biol. 1993;12(8):715–727. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez IR, Mazuruk K, Schoen TJ, Chader GJ. Structural analysis of the human hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase gene. Presence of two distinct promoters. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(50):31969–31977. - PubMed
-
- Montange MF, Champier J, Szathmari A, Wierinckx A, Mottolese C, Guyotat J, Branger DF, Jouvet J, Lachuer A. Microarray analysis reveals differential gene expression patterns in tumors of the pineal region. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006;65(7):675–684. - PubMed
-
- Srinivasan V, Smits M, Spence W, Lowe AD, Kayumov L, Perumal SRP, Parry B, Cardinali DP. Melatonin in mood disorders. World J Biol Psychia. 2006;7(3):138–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

