Imaging in anatomy: a comparison of imaging techniques in embalmed human cadavers
- PMID: 24156510
- PMCID: PMC4016606
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6920-13-143
Imaging in anatomy: a comparison of imaging techniques in embalmed human cadavers
Abstract
Background: A large variety of imaging techniques is an integral part of modern medicine. Introducing radiological imaging techniques into the dissection course serves as a basis for improved learning of anatomy and multidisciplinary learning in pre-clinical medical education.
Methods: Four different imaging techniques (ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging) were performed in embalmed human body donors to analyse possibilities and limitations of the respective techniques in this peculiar setting.
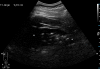
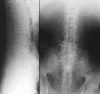
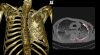
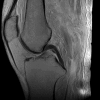
Results: The quality of ultrasound and radiography images was poor, images of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging were of good quality.
Conclusion: Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging have a superior image quality in comparison to ultrasound and radiography and offer suitable methods for imaging embalmed human cadavers as a valuable addition to the dissection course.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postmortem computed tomography of cadavers embalmed for use in teaching gross anatomy.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2006 Nov-Dec;30(6):949-54. doi: 10.1097/01.rct.0000232473.30033.c8. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2006. PMID: 17082701
-
Learning anatomy through Thiel- vs. formalin-embalmed cadavers: Student perceptions of embalming methods and effect on functional anatomy knowledge.Anat Sci Educ. 2018 Mar;11(2):166-174. doi: 10.1002/ase.1715. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Anat Sci Educ. 2018. PMID: 28719722
-
Integration of medical imaging including ultrasound into a new clinical anatomy curriculum.Anat Sci Educ. 2015 May-Jun;8(3):205-20. doi: 10.1002/ase.1481. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Anat Sci Educ. 2015. PMID: 25132661
-
Cadaveric dissection as an educational tool for anatomical sciences in the 21st century.Anat Sci Educ. 2017 Jun;10(3):286-299. doi: 10.1002/ase.1649. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Anat Sci Educ. 2017. PMID: 27574911 Review.
-
Skeletal muscle imaging and inflammatory myopathies.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007 Nov;19(6):530-5. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e3282efdc66. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17917531 Review.
Cited by
-
The tell-tale thigh.BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Mar 29;2016:bcr2015212909. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2015-212909. BMJ Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27216934 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging assessment of lateral atlantoaxial joint meniscoid composition: a validation study.Eur Spine J. 2019 May;28(5):1180-1187. doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-05868-0. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Eur Spine J. 2019. PMID: 30604294
-
Comparison between pre-mortem and post-mortem cadaveric images for use with augmented reality headsets during dissection.Surg Radiol Anat. 2023 Oct;45(10):1311-1319. doi: 10.1007/s00276-023-03239-z. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Surg Radiol Anat. 2023. PMID: 37698598
-
Glenoid morphology in light of anatomical and reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a dissection- and 3D-CT-based study in male and female body donors.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Jan 10;18(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1373-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28068966 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging of viral pathogenesis and opportunities for the future.Npj Imaging. 2025;3(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s44303-024-00056-w. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Npj Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39872292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McLachlan JC. New path for teaching anatomy: living anatomy and medical imaging vs. dissection. Anat Rec B New Anat. 2004;13:4–5. - PubMed
-
- Entius CAC, van Rijn RR, Zwamborn AW, Kleinrensink GJ, Robben SGF. Influence of formaldehyde/ phenol fixation on MRI of the stifle joint and correlation with plastinated slices. J Int Soc Plastination. 2004;13:26–32.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

