The scale and evolutionary significance of horizontal gene transfer in the choanoflagellate Monosiga brevicollis
- PMID: 24156600
- PMCID: PMC4046809
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-729
The scale and evolutionary significance of horizontal gene transfer in the choanoflagellate Monosiga brevicollis
Abstract
Background: It is generally agreed that horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is common in phagotrophic protists. However, the overall scale of HGT and the cumulative impact of acquired genes on the evolution of these organisms remain largely unknown.
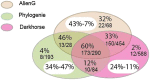
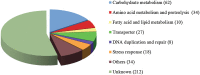
Results: Choanoflagellates are phagotrophs and the closest living relatives of animals. In this study, we performed phylogenomic analyses to investigate the scale of HGT and the evolutionary importance of horizontally acquired genes in the choanoflagellate Monosiga brevicollis. Our analyses identified 405 genes that are likely derived from algae and prokaryotes, accounting for approximately 4.4% of the Monosiga nuclear genome. Many of the horizontally acquired genes identified in Monosiga were probably acquired from food sources, rather than by endosymbiotic gene transfer (EGT) from obsolete endosymbionts or plastids. Of 193 genes identified in our analyses with functional information, 84 (43.5%) are involved in carbohydrate or amino acid metabolism, and 45 (23.3%) are transporters and/or involved in response to oxidative, osmotic, antibiotic, or heavy metal stresses. Some identified genes may also participate in biosynthesis of important metabolites such as vitamins C and K12, porphyrins and phospholipids.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that HGT is frequent in Monosiga brevicollis and might have contributed substantially to its adaptation and evolution. This finding also highlights the importance of HGT in the genome and organismal evolution of phagotrophic eukaryotes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of horizontal gene transfer in the genome of the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 16;11(1):5993. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85259-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33727612 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontal gene transfer in choanoflagellates.J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2013 Jan;320(1):1-9. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.22480. Epub 2012 Sep 19. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2013. PMID: 22997182 Review.
-
Choanoflagellate models - Monosiga brevicollis and Salpingoeca rosetta.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Aug;39:42-47. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.05.016. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27318693 Review.
-
Horizontally acquired DAP pathway as a unit of self-regulation.J Evol Biol. 2011 Mar;24(3):587-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2010.02192.x. Epub 2010 Dec 16. J Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21159005
-
Algal genes in the closest relatives of animals.Mol Biol Evol. 2010 Dec;27(12):2879-89. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq175. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Mol Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20627874
Cited by
-
Detection of horizontal gene transfer in the genome of the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 16;11(1):5993. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85259-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33727612 Free PMC article.
-
The cell survival pathways of the primordial RNA-DNA complex remain conserved in the extant genomes and may function as proto-oncogenes.Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2015 Mar;5(1):25-43. doi: 10.1556/EUJMI-D-14-00034. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2015. PMID: 25883792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Horizontal gene transfer: building the web of life.Nat Rev Genet. 2015 Aug;16(8):472-82. doi: 10.1038/nrg3962. Nat Rev Genet. 2015. PMID: 26184597 Review.
-
A genomic survey of transposable elements in the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta reveals selection on codon usage.Mob DNA. 2019 Nov 23;10:44. doi: 10.1186/s13100-019-0189-9. eCollection 2019. Mob DNA. 2019. PMID: 31788034 Free PMC article.
-
Independent evolution of complex development in animals and plants: deep homology and lateral gene transfer.Dev Genes Evol. 2019 Jan;229(1):25-34. doi: 10.1007/s00427-019-00626-8. Epub 2019 Jan 26. Dev Genes Evol. 2019. PMID: 30685797
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

