Engineering biodegradable and multifunctional peptide-based polymers for gene delivery
- PMID: 24156736
- PMCID: PMC4015834
- DOI: 10.1186/1754-1611-7-25
Engineering biodegradable and multifunctional peptide-based polymers for gene delivery
Abstract
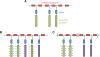
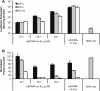
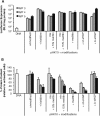
The complex nature of in vivo gene transfer establishes the need for multifunctional delivery vectors capable of meeting these challenges. An additional consideration for clinical translation of synthetic delivery formulations is reproducibility and scale-up of materials. In this review, we summarize our work over the last five years in developing a modular approach for synthesizing peptide-based polymers. In these materials, bioactive peptides that address various barriers to gene delivery are copolymerized with a hydrophilic backbone of N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA) using reversible-addition fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) polymerization. We demonstrate that this synthetic approach results in well-defined, narrowly-disperse polymers with controllable composition and molecular weight. To date, we have investigated the effectiveness of various bioactive peptides for DNA condensation, endosomal escape, cell targeting, and degradability on gene transfer, as well as the impact of multivalency and polymer architecture on peptide bioactivity.
Figures
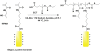

Similar articles
-
Synthesis of statistical copolymers containing multiple functional peptides for nucleic Acid delivery.Biomacromolecules. 2010 Nov 8;11(11):3007-13. doi: 10.1021/bm100806h. Epub 2010 Oct 5. Biomacromolecules. 2010. PMID: 20923198 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable HPMA-oligolysine copolymers for improved gene delivery.Bioconjug Chem. 2010 Jan;21(1):140-50. doi: 10.1021/bc9003662. Bioconjug Chem. 2010. PMID: 19968270 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide] via Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization as Safe Nanocarrier.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016 Jun;16(6):5746-54. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2016.11749. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27427626
-
Exploring the role of peptides in polymer-based gene delivery.Acta Biomater. 2017 Sep 15;60:23-37. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.07.043. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28778533 Review.
-
Biomedical applications of polymers derived by reversible addition - fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT).Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Aug 30;91:141-52. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.016. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 26050529 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation, purification and engineering of extracellular vesicles and their biomedical applications.Methods. 2020 May 1;177:114-125. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.11.012. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Methods. 2020. PMID: 31790730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic delivery of the tumor necrosis factor gene to tumors by a novel dual DNA-nanocomplex in a nanoparticle system.Nanomedicine. 2017 Jul;13(5):1833-1839. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2017.03.004. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28343015 Free PMC article.
-
Structure Dependence of Lysosomal Transit of Chitosan-Based Polyplexes for Gene Delivery.Mol Biotechnol. 2016 Oct;58(10):648-656. doi: 10.1007/s12033-016-9964-8. Mol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27412655
-
Covalent nano delivery systems for selective imaging and treatment of brain tumors.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017 Apr;113:177-200. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 10. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017. PMID: 28606739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomolecular Densely Grafted Brush Polymers: Oligonucleotides, Oligosaccharides and Oligopeptides.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Nov 2;59(45):19762-19772. doi: 10.1002/anie.202005379. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32436259 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

