Immunopurification of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) proteins
- PMID: 24156781
- PMCID: PMC4015550
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-429
Immunopurification of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) proteins
Abstract
Background: The adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumour suppressor gene encodes a 2843 residue (310 kDa) protein. APC is a multifunctional protein involved in the regulation of β-catenin/Wnt signalling, cytoskeletal dynamics and cell adhesion. APC mutations occur in most colorectal cancers and typically result in truncation of the C-terminal half of the protein.
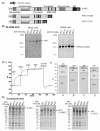
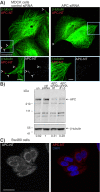
Results: In order to investigate the biophysical properties of APC, we have generated a set of monoclonal antibodies which enable purification of recombinant forms of APC. Here we describe the characterisation of these anti-APC monoclonal antibodies (APC-NT) that specifically recognise endogenous APC both in solution and in fixed cells. Full-length APC(1-2843) and cancer-associated, truncated APC proteins, APC(1-1638) and APC(1-1311) were produced in Sf9 insect cells.
Conclusions: Recombinant APC proteins were purified using a two-step affinity approach using our APC-NT antibodies. The purification of APC proteins provides the basis for detailed structure/function analyses of full-length, cancer-truncated and endogenous forms of the protein.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of a Wnt-induced protein complex by affinity proteomics using an antibody that recognizes a sub-population of β-catenin.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1824(7):925-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.03.006. Epub 2012 Mar 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22469663
-
N-terminal truncation mutations of adenomatous polyposis coli are associated with primary cilia defects.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;55:79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.08.010. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25150829
-
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) membrane recruitment 3, a member of the APC membrane recruitment family of APC-binding proteins, is a positive regulator of Wnt-β-catenin signalling.FEBS J. 2014 Feb;281(3):787-801. doi: 10.1111/febs.12624. Epub 2013 Dec 12. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24251807
-
Involvement of adenomatous polyposis coli in colorectal tumorigenesis.Front Biosci. 2005 May 1;10:1118-34. doi: 10.2741/1605. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15769611 Review.
-
[Familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome (FAP): pathogenesis and molecular mechanisms].Med Klin (Munich). 2003 Dec 15;98(12):776-82. doi: 10.1007/s00063-003-1325-2. Med Klin (Munich). 2003. PMID: 14685680 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Technical considerations in PCR-based assay design for diagnostic DNA methylation cancer biomarkers.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Apr 27;14(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01273-z. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 35477541 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of APC truncation involved in colorectal cancer tumorigenesis (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 Oct 15;29(1):2. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14748. eCollection 2025 Jan. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39526304 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giles RH, Van Es JH, Clevers H. Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;6(1):1–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

