Mast cell-deficient kit mice develop house dust mite-induced lung inflammation despite impaired eosinophil recruitment
- PMID: 24157568
- PMCID: PMC6741476
- DOI: 10.1159/000354984
Mast cell-deficient kit mice develop house dust mite-induced lung inflammation despite impaired eosinophil recruitment
Abstract
Background: Mast cells are implicated in allergic and innate immune responses in asthma, although their role in models using an allergen relevant for human disease is incompletely understood. House dust mite (HDM) allergy is common in asthma patients. Our aim was to investigate the role of mast cells in HDM-induced allergic lung inflammation.
Methods: Wild-type (Wt) and mast cell-deficient Kit(w-sh) mice on a C57BL/6 background were repetitively exposed to HDM via the airways.
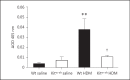
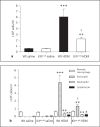
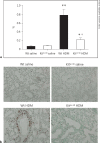
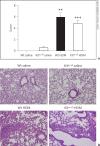
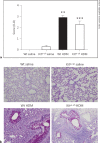
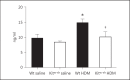
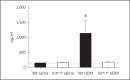
Results: HDM challenge resulted in a rise in tryptase activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of Wt mice, indicative of mast cell activation. Kit(w-sh) mice showed a strongly attenuated HDM- induced recruitment of eosinophils in BALF and lung tissue, accompanied by reduced pulmonary levels of the eosinophil chemoattractant eotaxin. Remarkably, Kit(w-sh) mice demonstrated an unaltered capacity to develop lung pathology and increased mucus production in response to HDM. The increased plasma IgE in response to HDM in Wt mice was absent in Kit(w-sh) mice.
Conclusion: These data contrast with previous reports on the role of mast cells in models using ovalbumin as allergen in that C57BL/6 Kit(w-sh) mice display a selective impairment of eosinophil recruitment without differences in other features of allergic inflammation.
Copyright © 2013 S. Karger AG, Basel
Figures
References
-
- Braman SS. The global burden of asthma. Chest. 2006;130:4S–12S. - PubMed
-
- Murphy DM, O'Byrne PM. Recent advances in the pathophysiology of asthma. Chest. 2010;137:1417–1426. - PubMed
-
- Nelson RP, Jr, DiNicolo R, Fernandez-Caldas E, Seleznick MJ, Lockey RF, Good RA. Allergen-specific IgE levels and mite allergen exposure in children with acute asthma first seen in an emergency department and in nonasthmatic control subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98:258–263. - PubMed
-
- Lodge CJ, Lowe AJ, Gurrin LC, Hill DJ, Hosking CS, Khalafzai RU, Hopper JL, Matheson MC, Abramson MJ, Allen KJ, Dharmage SC. House dust mite sensitization in toddlers predicts current wheeze at age 12 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:782–788. e9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

