APR-246/PRIMA-1MET inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 and converts the enzyme to a dedicated NADPH oxidase
- PMID: 24157875
- PMCID: PMC3920950
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.417
APR-246/PRIMA-1MET inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 and converts the enzyme to a dedicated NADPH oxidase
Erratum in
-
APR-246/PRIMA-1MET inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 and converts the enzyme to a dedicated NADPH oxidase.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Apr 13;8(4):e2751. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.137. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28406483 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
The low-molecular-weight compound APR-246 (PRIMA-1(MET)) restores wild-type conformation and function to mutant p53, and triggers apoptosis in tumor cells. We show here that APR-246 also targets the selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1), a key regulator of cellular redox balance. APR-246 inhibited both recombinant TrxR1 in vitro and TrxR1 in cells. A Sec-to-Cys mutant of TrxR1 was not inhibited by APR-246, suggesting targeting of the selenocysteine residue in wild-type TrxR1. Preheated APR-246 and its conversion product methylene quinuclidinone (MQ) were much more efficient TrxR1 inhibitors than APR-246 itself, indicating that MQ is the active compound responsible for TrxR1 enzyme inhibition. TrxR1 inhibited by MQ was still functional as a pro-oxidant NADPH oxidase. Knockdown of TrxR1 caused a partial and reproducible attenuation of APR-246-induced tumor cell death independently of p53 status. Cellular TrxR1 activity was also inhibited by APR-246 irrespective of p53 status. We show that APR-246 can directly affect cellular redox status via targeting of TrxR1. Our findings provide an explanation for the previously observed effects of APR-246 on tumor cells lacking mutant p53.
Figures


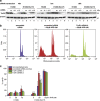
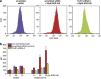
References
-
- Hussain SP, Harris CC. P53 mutation spectrum and load: the generation of hypotheses linking the exposure of endogenous or exogenous carcinogens to human cancer. Mutat Res. 1999;428:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Petitjean A, Mathe E, Kato S, Ishioka C, Tavtigian SV, Hainaut P, et al. Impact of mutant p53 functional properties on TP53 mutation patterns and tumor phenotype: lessons from recent developments in the IARC TP53 database. Hum Mut. 2007;28:622–629. - PubMed
-
- Soussi T, Wiman KG. Shaping genetic alterations in human cancer: the p53 mutation paradigm. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:303–312. - PubMed
-
- Petitjean A, Achatz MI, Borresen-Dale AL, Hainaut P, Olivier M. TP53 mutations in human cancers: functional selection and impact on cancer prognosis and outcomes. Oncogene. 2007;26:2157–2165. - PubMed
-
- Blandino G, Levine AJ, Oren M. Mutant p53 gain of function: differential effects of different p53 mutants on resistance of cultured cells to chemotherapy. Oncogene. 1999;18:477–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

