EGCG inhibit chemical reactivity of iron through forming an Ngal-EGCG-iron complex
- PMID: 24158698
- PMCID: PMC4416964
- DOI: 10.1007/s10534-013-9681-8
EGCG inhibit chemical reactivity of iron through forming an Ngal-EGCG-iron complex
Abstract
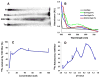
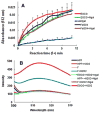
Accumulated evidence indicates that the interconversion of iron between ferric (Fe(3+)) and ferrous (Fe(2+)) can be realized through interaction with reactive oxygen species in the Fenton and Haber-Weiss reactions and thereby physiologically effects redox cycling. The imbalance of iron and ROS may eventually cause tissue damage such as renal proximal tubule injury and necrosis. Many approaches were exploited to ameliorate the oxidative stress caused by the imbalance. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, the most active and most abundant catechin in tea, was found to be involved in the protection of a spectrum of renal injuries caused by oxidative stress. Most of studies suggested that EGCG works as an antioxidant. In this paper, Multivariate analysis of the LC-MS data of tea extracts and binding assays showed that the tea polyphenol EGCG can form stable complex with iron through the protein Ngal, a biomarker of acute kidney injury. UV-Vis and Luminescence spectrum methods showed that Ngal can inhibit the chemical reactivity of iron and EGCG through forming an Ngal-EGCG-iron complex. In thinking of the interaction of iron and ROS, we proposed that EGCG may work as both antioxidant and Ngal binding siderphore in protection of kidney from injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
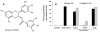

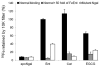
References
-
- Abdel-Raheem IT, El-Sherbiny GA, Taye A. Green tea ameliorates renal oxidative damage induced by gentamicin in rats. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2010;23:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Balentine DA, Wiseman SA, Bouwens LC. The chemistry of tea flavonoids. Crit Rev Food Sci. 1997;37:693–704. - PubMed
-
- de Vries B, Walter SJ, von Bonsdorff L, Wolfs TGAM, et al. Reduction of circulating redox-active iron by apotransferrin protects against renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Transplantation. 2004;77:669–675. - PubMed
-
- El-Mowafy AM, Al-Gayyar MM, Salem HA, El-Mesery ME, Darweish MM. Novel chemotherapeutic and renal protective effects for the green tea (EGCG): role of oxidative stress and inflammatory-cytokine signaling. Phytomedicine. 2010;17:1067–1075. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

