MicroRNA-214 antagonism protects against renal fibrosis
- PMID: 24158985
- PMCID: PMC3871772
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013010072
MicroRNA-214 antagonism protects against renal fibrosis
Abstract
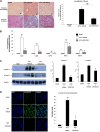
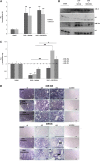
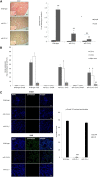
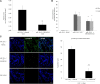
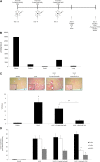
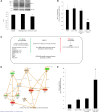
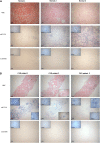
Renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis is the common end point of progressive renal disease. MicroRNA (miR)-214 and miR-21 are upregulated in models of renal injury, but the function of miR-214 in this setting and the effect of its manipulation remain unknown. We assessed the effect of inhibiting miR-214 in an animal model of renal fibrosis. In mice, genetic deletion of miR-214 significantly attenuated interstitial fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Treatment of wild-type mice with an anti-miR directed against miR-214 (anti-miR-214) before UUO resulted in similar antifibrotic effects, and in vivo biodistribution studies demonstrated that anti-miR-214 accumulated at the highest levels in the kidney. Notably, in vivo inhibition of canonical TGF-β signaling did not alter the regulation of endogenous miR-214 or miR-21. Whereas miR-21 antagonism blocked Smad 2/3 activation, miR-214 antagonism did not, suggesting that miR-214 induces antifibrotic effects independent of Smad 2/3. Furthermore, TGF-β blockade combined with miR-214 deletion afforded additional renal protection. These phenotypic effects of miR-214 depletion were mediated through broad regulation of the transcriptional response to injury, as evidenced by microarray analysis. In human kidney tissue, miR-214 was detected in cells of the glomerulus and tubules as well as in infiltrating immune cells in diseased tissue. These studies demonstrate that miR-214 functions to promote fibrosis in renal injury independent of TGF-β signaling in vivo and that antagonism of miR-214 may represent a novel antifibrotic treatment in the kidney.
Figures

References
-
- Bohle A, Mackensen-Haen S, von Gise H: Significance of tubulointerstitial changes in the renal cortex for the excretory function and concentration ability of the kidney: A morphometric contribution. Am J Nephrol 7: 421–433, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Liu Y: Renal fibrosis: New insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int 69: 213–217, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Eddy AA, Neilson EG: Chronic kidney disease progression. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 2964–2966, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Sharma K, Jin Y, Guo J, Ziyadeh FN: Neutralization of TGF-beta by anti-TGF-beta antibody attenuates kidney hypertrophy and the enhanced extracellular matrix gene expression in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes 45: 522–530, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Grygielko ET, Martin WM, Tweed C, Thornton P, Harling J, Brooks DP, Laping NJ: Inhibition of gene markers of fibrosis with a novel inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β type I receptor kinase in puromycin-induced nephritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313: 943–951, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

