Fibroblast growth factor-23 and cardiovascular events in CKD
- PMID: 24158986
- PMCID: PMC3904568
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013050465
Fibroblast growth factor-23 and cardiovascular events in CKD
Abstract
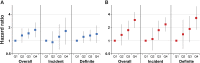
An elevated level of fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23) is the earliest abnormality of mineral metabolism in CKD. High FGF-23 levels promote left ventricular hypertrophy but not coronary artery calcification. We used survival analysis to determine whether elevated FGF-23 is associated with greater risk of adjudicated congestive heart failure (CHF) and atherosclerotic events (myocardial infarction, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease) in a prospective cohort of 3860 participants with CKD stages 2-4 (baseline estimated GFR [eGFR], 44±15 ml/min per 1.73 m(2)). During a median follow-up of 3.7 years, 360 participants were hospitalized for CHF (27 events/1000 person-years) and 287 had an atherosclerotic event (22 events/1000 person-years). After adjustment for demographic characteristics, kidney function, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and medications, higher FGF-23 was independently associated with graded risk of CHF (hazard ratio [HR], 1.45 per doubling [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.28 to 1.65]; HR for highest versus lowest quartile, 2.98 [95% CI, 1.97 to 4.52]) and atherosclerotic events (HR per doubling, 1.24 [95% CI, 1.09 to 1.40]; HR for highest versus lowest quartile, 1.76 [95% CI, 1.20 to 2.59]). Elevated FGF-23 was associated more strongly with CHF than with atherosclerotic events (P=0.02), and uniformly was associated with greater risk of CHF events across subgroups stratified by eGFR, proteinuria, prior heart disease, diabetes, BP control, anemia, sodium intake, income, fat-free mass, left ventricular mass index, and ejection fraction. Thus, higher FGF-23 is independently associated with greater risk of cardiovascular events, particularly CHF, in patients with CKD stages 2-4.
Figures



References
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Levey AS: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298: 2038–2047, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Matsushita K, van der Velde M, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, Gansevoort RT, Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium : Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: A collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet 375: 2073–2081, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Tonelli M, Muntner P, Lloyd A, Manns BJ, Klarenbach S, Pannu N, James MT, Hemmelgarn BR, Alberta Kidney Disease Network : Risk of coronary events in people with chronic kidney disease compared with those with diabetes: A population-level cohort study. Lancet 380: 807–814, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Kottgen A, Russell SD, Loehr LR, Crainiceanu CM, Rosamond WD, Chang PP, Chambless LE, Coresh J: Reduced kidney function as a risk factor for incident heart failure: The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 1307–1315, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HL107241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076116/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK092353/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073665/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23DK095949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54TR000255/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK073665/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK094796/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK092353/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK076116/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-16500,/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK095949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K24DK093723/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081374/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK093723/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK094796/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK087858/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK081374/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

