Efficacy and safety of QVA149 compared to the concurrent administration of its monocomponents indacaterol and glycopyrronium: the BEACON study
- PMID: 24159259
- PMCID: PMC3805248
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S49615
Efficacy and safety of QVA149 compared to the concurrent administration of its monocomponents indacaterol and glycopyrronium: the BEACON study
Erratum in
- Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014;9:85. Dosage error in published abstract; MEDLINE/PubMed abstract corrected; Dosage error in article text
Abstract
Introduction: The BEACON study evaluated the efficacy and safety of QVA149, a once-daily dual bronchodilator containing a fixed-dose combination of the long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) indacaterol and long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrronium (NVA237), in development for the treatment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), compared with the free-dose concurrent administration of indacaterol plus glycopyrronium (IND+GLY).
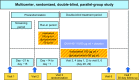
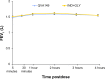
Methods: In this multicenter, double-blind, parallel group study, patients with stage II or stage III COPD (Global initiative for chronic Obstructive Lung Disease [GOLD] 2010) were randomized (1:1) to once-daily QVA149 (110 μg indacaterol/50 μg glycopyrronium) or concurrent administration of indacaterol (150 μg) and glycopyrronium (50 μg) via the Breezhaler® device (Novartis AG, Basel, Switzerland) for 4 weeks. The primary endpoint was to evaluate the noninferiority of QVA149 as compared with concurrent administration of IND+GLY, for trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) after 4 weeks of treatment. The other assessments included FEV1 area under the curve from 0 to 4 hours (AUC0-4 hours) at day 1 and week 4, symptom scores, rescue medication use, safety, and tolerability over the 4-week study period.
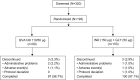
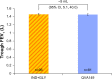
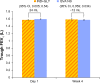
Results: Of 193 patients randomized, 187 (96.9%) completed the study.Trough FEV1 at week 4 for QVA149 and IND+GLY was 1.5 L ± 0.02 [DOSAGE ERROR CORRECTED] and 1.46 L ± 0.18, respectively. The FEV1 AUC0-4 hours at day 1 and week 4 were similar between the two treatment groups. Both treatment groups had a similar reduction in symptom scores and rescue medication use for the 4-week treatment period. Overall, 25.6% of patients in QVA149 group and 25.2% in the IND+GLY group experienced an adverse event, with the majority being mild-to-moderate in severity. No deaths were reported during the study or during the 30 days follow-up period.
Conclusion: The BEACON study demonstrated that once-daily QVA149 provides an efficacy and safety profile similar to the concurrent administration of its monocomponents indacaterol and glycopyrronium.
Keywords: COPD; FEV1 AUC0–4 hours; LABA; LAMA; rescue medication.
Figures
References
-
- Global initiative for chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2010 update Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease, Inc; 2010Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org/uploads/users/files/GOLDReport_April112011.pdfAccessed on July 20, 2012
-
- Mahler DA, D’Urzo A, Bateman ED, et al. INTRUST-1 and INTRUST-2 study investigators Concurrent use of indacaterol plus tiotropium in patients with COPD provides superior bronchodilation compared with tiotropium alone: a randomised, double-blind comparison. Thorax. 2012;67(9):781–788. - PubMed
-
- Rabe KF, Timmer W, Sagkriotis A, Viel K. Comparison of a combination of tiotropium plus formoterol to salmeterol plus fluticasone in moderate COPD. Chest. 2008;134(2):255–262. - PubMed
-
- Tashkin DP, Celli BR, Decramer M, Lystig T, Liu D, Kesten S. Efficacy of tiotropium in COPD patients with FEV1 ≥ 60% participating in the UPLIFT® trial. COPD. 2012;9(3):289–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

