InterVA versus Spectrum: how comparable are they in estimating AIDS mortality patterns in Nairobi's informal settlements?
- PMID: 24160914
- PMCID: PMC3809385
- DOI: 10.3402/gha.v6i0.21638
InterVA versus Spectrum: how comparable are they in estimating AIDS mortality patterns in Nairobi's informal settlements?
Abstract
Background: The Spectrum computer package is used to generate national AIDS mortality estimates in settings where vital registration systems are lacking. Similarly, InterVA-4 (the latest version of the InterVA programme) is used to estimate cause-of-mortality data in countries where cause-specific mortality data are not available.
Objective: This study aims to compare trends in adult AIDS-related mortality estimated by Spectrum with trends from the InterVA-4 programme applied to data from a Health and Demographic Surveillance System (HDSS) in Nairobi, Kenya.
Design: A Spectrum model was generated for the city of Nairobi based on HIV prevalence data for Nairobi and national antiretroviral therapy coverage, underlying mortality, and migration assumptions. We then used data, generated through verbal autopsies, on 1,799 deaths that occurred in the HDSS area from 2003 to 2010 among adults aged 15-59. These data were then entered into InterVA-4 to estimate causes of death using probabilistic modelling. Estimates of AIDS-related mortality rates and all-cause mortality rates from Spectrum and InterVA-4 were compared and presented as annualised trends.
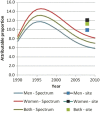
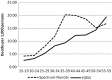
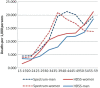
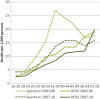
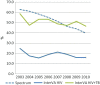
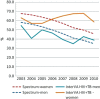
Results: Spectrum estimated that HIV prevalence in Nairobi was 7%, while the HDSS site measured 12% in 2010. Despite this difference, Spectrum estimated higher levels of AIDS-related mortality. Between 2003 and 2010, the proportion of AIDS-related mortality in Nairobi decreased from 63 to 40% according to Spectrum and from 25 to 16% according to InterVA. The net AIDS-related mortality in Spectrum was closer to the combined mortality rates when AIDS and tuberculosis (TB) deaths were included for InterVA-4.
Conclusion: Overall trends in AIDS-related deaths from both methods were similar, although the values were closer when TB deaths were included in InterVA. InterVA-4 might not accurately differentiate between TB and AIDS deaths.
Keywords: AIDS; InterVA; Nairobi; Spectrum; mortality.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trends in Causes of Adult Deaths among the Urban Poor: Evidence from Nairobi Urban Health and Demographic Surveillance System, 2003-2012.J Urban Health. 2015 Jun;92(3):422-45. doi: 10.1007/s11524-015-9943-6. J Urban Health. 2015. PMID: 25758599 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the InterVA model for determining AIDS mortality from verbal autopsies in the adult population of Addis Ababa.Trop Med Int Health. 2010 May;15(5):547-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2010.02484.x. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Trop Med Int Health. 2010. PMID: 20214760 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in non-communicable disease mortality among adult residents in Nairobi's slums, 2003-2011: applying InterVA-4 to verbal autopsy data.Glob Health Action. 2014 Oct 29;7:25533. doi: 10.3402/gha.v7.25533. eCollection 2014. Glob Health Action. 2014. PMID: 25377336 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of AIDS on adult mortality: evidence from national and regional statistics.AIDS. 2004 Jun;18 Suppl 2:S19-26. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200406002-00003. AIDS. 2004. PMID: 15319740 Review.
-
Updates to the spectrum model to estimate key HIV indicators for adults and children.AIDS. 2014 Nov;28 Suppl 4(4):S427-34. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000483. AIDS. 2014. PMID: 25406748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Measuring HIV-related mortality in the first decade of anti-retroviral therapy in sub-Saharan Africa.Glob Health Action. 2014 May 21;7:24787. doi: 10.3402/gha.v7.24787. eCollection 2014. Glob Health Action. 2014. PMID: 24852247 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Does the Spectrum model accurately predict trends in adult mortality? Evaluation of model estimates using empirical data from a rural HIV community cohort study in North-Western Tanzania.Glob Health Action. 2014 Jan 16;7:21783. doi: 10.3402/gha.v7.21783. eCollection 2014. Glob Health Action. 2014. PMID: 24438873 Free PMC article.
-
Embracing different approaches to estimating HIV incidence, prevalence and mortality.AIDS. 2014 Nov;28 Suppl 4(4):S523-32. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000488. AIDS. 2014. PMID: 25406755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in Causes of Adult Deaths among the Urban Poor: Evidence from Nairobi Urban Health and Demographic Surveillance System, 2003-2012.J Urban Health. 2015 Jun;92(3):422-45. doi: 10.1007/s11524-015-9943-6. J Urban Health. 2015. PMID: 25758599 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring causes of adult mortality in rural northern Malawi over a decade of change.Glob Health Action. 2014 Apr 30;7:23621. doi: 10.3402/gha.v7.23621. eCollection 2014. Glob Health Action. 2014. PMID: 24802384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS. Global report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic; Geneva: UNAIDS; 2012.
-
- Futures Institute. Glastonbury, CT: Futures Institute; 2012. Kenya National Spectrum file 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
