Impact of new sequencing technologies on studies of the human B cell repertoire
- PMID: 24161653
- PMCID: PMC3882336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.09.010
Impact of new sequencing technologies on studies of the human B cell repertoire
Figures

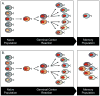
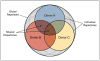
References
-
- Lefranc M-P, Lefranc G. The Immunoglobulin FactsBook. Academic Press; 2001.
-
- Crotty S, Ahmed R. Immunological memory in humans. Sem Immunol. 2004;16:197–203. - PubMed
-
- Krause JC, Tsibane T, Tumpey TM, Huffman CJ, Briney BS, Smith SA, Basler CF, Crowe JE., Jr Epitope-specific human influenza antibody repertoires diversify by B cell intraclonal sequence divergence and interclonal convergence. J Immunol. 2011;187:3704–11. This is one of the first papers to reveal the persistence of highly related somatic variants of antibodies within clones responding to a virus, and also shows that genetically related but independent clones converge on common sequences during epitope-specific responses. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

