Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli on flies at poultry farms
- PMID: 24162567
- PMCID: PMC3910986
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02616-13
Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli on flies at poultry farms
Abstract
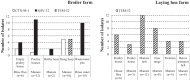
In the Netherlands, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli bacteria are highly prevalent in poultry, and chicken meat has been implicated as a source of ESBL-producing E. coli present in the human population. The current study describes the isolation of ESBL-producing E. coli from house flies and blow flies caught at two poultry farms, offering a potential alternative route of transmission of ESBL-producing E. coli from poultry to humans. Overall, 87 flies were analyzed in 19 pools. ESBL-producing E. coli bacteria were detected in two fly pools (10.5%): a pool of three blow flies from a broiler farm and a pool of eight house flies from a laying-hen farm. From each positive fly pool, six isolates were characterized and compared with isolates obtained from manure (n = 53) sampled at both farms and rinse water (n = 10) from the broiler farm. Among six fly isolates from the broiler farm, four different types were detected with respect to phylogenetic group, sequence type (ST), and ESBL genotype: A0/ST3519/SHV-12, A1/ST10/SHV-12, A1/ST58/SHV-12, and B1/ST448/CTX-M-1. These types, as well as six additional types, were also present in manure and/or rinse water at the same farm. At the laying-hen farm, all fly and manure isolates were identical, carrying blaTEM-52 in an A1/ST48 genetic background. The data imply that flies acquire ESBL-producing E. coli at poultry farms, warranting further evaluation of the contribution of flies to dissemination of ESBL-producing E. coli in the community.
Figures

References
-
- Cantón R, Akova M, Carmeli Y, Giske CG, Glupczynski Y, Gniadkowski M, Livermore DM, Miriagou V, Naas T, Rossolini GM, Samuelsen O, Seifert H, Woodford N, Nordmann P. 2012. Rapid evolution and spread of carbapenemases among Enterobacteriaceae in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 18:413–431. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03821.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

