Transcriptional downregulation of S1pr1 is required for the establishment of resident memory CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 24162775
- PMCID: PMC3844557
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2745
Transcriptional downregulation of S1pr1 is required for the establishment of resident memory CD8+ T cells
Abstract
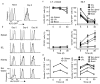
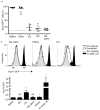
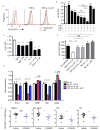
Cell-mediated immunity critically depends on the localization of lymphocytes at sites of infection. While some memory T cells recirculate, a distinct lineage (resident memory T cells (T(RM) cells)) are embedded in nonlymphoid tissues (NLTs) and mediate potent protective immunity. However, the defining transcriptional basis for the establishment of T(RM) cells is unknown. We found that CD8(+) T(RM) cells lacked expression of the transcription factor KLF2 and its target gene S1pr1 (which encodes S1P1, a receptor for sphingosine 1-phosphate). Forced expression of S1P1 prevented the establishment of T(RM) cells. Cytokines that induced a T(RM) cell phenotype (including transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), interleukin 33 (IL-33) and tumor-necrosis factor) elicited downregulation of KLF2 expression in a pathway dependent on phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase (PI(3)K) and the kinase Akt, which suggested environmental regulation. Hence, regulation of KLF2 and S1P1 provides a switch that dictates whether CD8(+) T cells commit to recirculating or tissue-resident memory populations.
Figures




Comment in
-
Tissue-resident T cells lose their S1P1 exit visas.Cell Mol Immunol. 2014 May;11(3):221-3. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.7. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Cell Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24561454 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Klonowski KD, et al. Dynamics of blood-borne CD8 memory T cell migration in vivo. Immunity. 2004;20:551–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

