Postprandial VLDL lipolysis products increase monocyte adhesion and lipid droplet formation via activation of ERK2 and NFκB
- PMID: 24163071
- PMCID: PMC3920150
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00137.2013
Postprandial VLDL lipolysis products increase monocyte adhesion and lipid droplet formation via activation of ERK2 and NFκB
Abstract
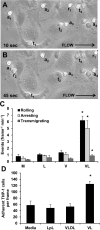
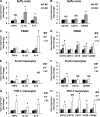
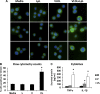
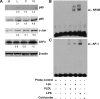
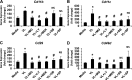
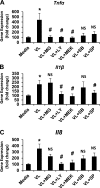
Postprandial lipemia is characterized by a transient increase in circulating triglyceride-rich lipoproteins such as very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and has been shown to activate monocytes in vivo. Lipolysis of VLDL releases remnant particles, phospholipids, monoglycerides, diglycerides, and fatty acids in close proximity to endothelial cells and monocytes. We hypothesized that postprandial VLDL lipolysis products could activate and recruit monocytes by increasing monocyte expression of proinflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules, and that such activation is related to the development of lipid droplets. Freshly isolated human monocytes were treated with VLDL lipolysis products (2.28 mmol/l triglycerides + 2 U/ml lipoprotein lipase), and monocyte adhesion to a primed endothelial monolayer was observed using a parallel plate flow chamber coupled with a CCD camera. Treated monocytes showed more rolling and adhesion than controls, and an increase in transmigration between endothelial cells. The increased adhesive events were related to elevated expression of key integrin complexes including Mac-1 [α(m)-integrin (CD11b)/β2-integrin (CD18)], CR4 [α(x)-integrin (CD11c)/CD18] and VLA-4 [α4-integrin (CD49d)/β1-integrin (CD29)] on treated monocytes. Treatment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and THP-1 monocytes with VLDL lipolysis products increased expression of TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-8 over controls, with concurrent activation of NFkB and AP-1. NFκB and AP-1-induced cytokine and integrin expression was dependent on ERK and Akt phosphorylation. Additionally, fatty acids from VLDL lipolysis products induced ERK2-dependent lipid droplet formation in monocytes, suggesting a link to inflammatory signaling pathways. These results provide novel mechanisms for postprandial monocyte activation by VLDL lipolysis products, suggesting new pathways and biomarkers for chronic, intermittent vascular injury.
Keywords: adhesion molecules; fatty acids; inflammation; lipoprotein lipase.
Figures


References
-
- Ali S, Mann DA. Signal transduction via the NF-kappaB pathway: a targeted treatment modality for infection, inflammation and repair. Cell Biochem Funct 22: 67–79, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Alipour A, van Oostrom AJ, Izraeljan A, Verseyden C, Collins JM, Frayn KN, Plokker TW, Elte JW, Castro Cabezas M. Leukocyte activation by triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28: 792–797, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Bermudez B, Lopez S, Varela LM, Ortega A, Pacheco YM, Moreda W, Moreno-Luna R, Abia R, Muriana FJ. Triglyceride-rich lipoprotein regulates APOB48 receptor gene expression in human THP-1 monocytes and macrophages. J Nutr 142: 227–232, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Bouwens M, Grootte Bromhaar M, Jansen J, Müller M, Afman LA. Postprandial dietary lipid-specific effects on human peripheral blood mononuclear cell gene expression profiles. Am J Clin Nutr 91: 208–217, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

