Loss to follow-up occurs at all stages in the diagnostic and follow-up period among HIV-infected patients in Guinea-Bissau: a 7-year retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 24163204
- PMCID: PMC3808780
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003499
Loss to follow-up occurs at all stages in the diagnostic and follow-up period among HIV-infected patients in Guinea-Bissau: a 7-year retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: To describe loss to follow-up (LTFU) at all stages of the HIV programme.
Design: A retrospective cohort study.
Setting: The HIV clinic at Hospital National Simão Mendes in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau.
Participants: A total of 4080 HIV-infected patients.
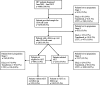
Outcome measures: Baseline characteristics, percentages and incidence rates of LTFU as well as LTFU risk factors at four different stages: immediately after HIV diagnosis (stage 1), after the first CD4 cell count and before a follow-up consultation (stage 2), after a follow-up consultation for patients not eligible for antiretroviral treatment (ART; stage 3) and LTFU among patients on ART (stage 4).
Results: Almost one-third of the patients were lost to the programme before the first consultation where ART initiation is decided; during the 7-year observation period, more than half of the patients had been lost to follow-up (overall incidence rate=51.1 patients lost per 100 person-years). Age below 30 years at inclusion was a risk factor for LTFU at all stages of the HIV programme. The biggest risk factors were body mass index <18.5 kg/m(2) (stage 1), male gender (stage 2), HIV-2 infection (stage 3) and CD4 cell count <200 cells/μL (stage 4).
Conclusions: In this study, LTFU constituted a major problem, and this may apply to other similar ART facilities. More than half of the patients were lost to follow-up shortly after enrolment, possibly implying a high mortality. Thus, retention should be given a high priority.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS Data Tables 2011 http://www.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/unaidspubl... (accessed 4 Jun 2013).
-
- Oyugi JH, Byakika-Tusiime J, Ragland K, et al. Treatment interruptions predict resistance in HIV-positive individuals purchasing fixed-dose combination antiretroviral therapy in Kampala, Uganda. AIDS 2007;21:965–71 - PubMed
-
- Adje C, Cheingsong R, Roels TH, et al. High prevalence of genotypic and phenotypic HIV-1 drug-resistant strains among patients receiving antiretroviral therapy in Abidjan, Cote d'Ivoire. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2001;26:501–6 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials