Bispectral index score and observer's assessment of awareness/sedation score may manifest divergence during onset of sedation: Study with midazolam and propofol
- PMID: 24163448
- PMCID: PMC3800326
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5049.118557
Bispectral index score and observer's assessment of awareness/sedation score may manifest divergence during onset of sedation: Study with midazolam and propofol
Abstract
Background: Correlation between the clinical and electroencephalogram-based monitoring has been documented sporadically during the onset of sedation. Propofol and midazolam have been studied individually using the observer's assessment of awareness/sedation (OAA/S) score and Bispectral index score (BIS). The present study was designed to compare the time to onset of sedation for propofol and midazolam using both BIS and OAA/S scores, and to find out any correlation.
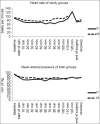
Methods: A total of 46 patients (18-60 years, either sex, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) I/II) posted for infraumbilical surgeries under spinal anaesthesia were randomly allocated to receive either injection propofol 1 mg/kg bolus followed by infusion 3 mg/kg/h (Group P, n=23) or injection midazolam 0.05 mg/kg bolus followed by infusion 0.06 mg/kg/h (Group M, n=23). Spinal anaesthesia was given with 2.5 ml to 3.0 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine heavy. When sensory block reached T6 level, sedation was initiated. The time to reach BIS score 70 and time to achieve OAA/S score 3 from the start of study drug were noted. OAA/S score at BIS score 70 was noted. Data from 43 patients were analyzed using SPSS 12 for Windows.
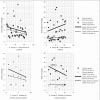
Results: Time to reach BIS score 70 using propofol was significantly lower than using the midazolam (P<0.05). Time to achieve OAA/S score 3 using propofol was comparable with midazolam (P=0.358).
Conclusion: A divergence exists between the time to reach BIS score 70 and time to achieve OAA/S score 3 using midazolam, compared with propofol, during the onset of sedation.
Keywords: Bispectral index score; midazolam; observer's assessment of awareness/sedation score; propofol; sedation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Brown DL. Spinal, epidural, and caudal anesthesia. In: Miller RD, editor. Miller's Anesthesia. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010. pp. 1612–27.
-
- Némethy M, Paroli L, Williams-Russo PG, Blanck TJ. Assessing sedation with regional anesthesia: Inter-rater agreement on a modified Wilson sedation scale. Anesth Analg. 2002;94:723–8. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Singh H, White PF. Electroencephalogram bispectral analysis predicts the depth of midazolam-induced sedation. Anesthesiology. 1996;84:64–9. - PubMed
-
- Arbour R. Using bispectral index monitoring to detect potential breakthrough awareness and limit duration of neuromuscular blockade. Am J Crit Care. 2004;13:66–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

