Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by a plumbagin derivative in estrogen positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- PMID: 24164046
- PMCID: PMC3894702
- DOI: 10.2174/18715206113136660369
Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by a plumbagin derivative in estrogen positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells
Abstract
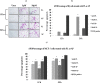
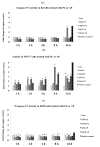
Plumbagin [5-hydroxy- 2-methyl-1, 4-naphthaquinone] is a well-known plant derived anticancer lead compound. Several efforts have been made to synthesize its analogs and derivatives in order to increase its anticancer potential. In the present study, plumbagin and its five derivatives have been evaluated for their antiproliferative potential in one normal and four human cancer cell lines. Treatment with derivatives resulted in dose- and time-dependent inhibition of growth of various cancer cell lines. Prescreening of compounds led us to focus our further investigations on acetyl plumbagin, which showed remarkably low toxicity towards normal BJ cells and HepG2 cells. The mechanisms of apoptosis induction were determined by APOPercentage staining, caspase-3/7 activation, reactive oxygen species production and cell cycle analysis. The modulation of apoptotic genes (p53, Mdm2, NF-kB, Bad, Bax, Bcl-2 and Casp-7) was also measured using real time PCR. The positive staining using APOPercentage dye, increased caspase-3/7 activity, increased ROS production and enhanced mRNA expression of proapoptotic genes suggested that acetyl plumbagin exhibits anticancer effects on MCF-7 cells through its apoptosis-inducing property. A key highlighting point of the study is low toxicity of acetyl plumbagin towards normal BJ cells and negligible hepatotoxicity (data based on HepG2 cell line). Overall results showed that acetyl plumbagin with reduced toxicity might have the potential to be a new lead molecule for testing against estrogen positive breast cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Plumbagin from a tropical pitcher plant (Nepenthes alata Blanco) induces apoptotic cell death via a p53-dependent pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.Food Chem Toxicol. 2019 Jan;123:492-500. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.11.040. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30458268
-
Targeting Cell Necroptosis and Apoptosis Induced by Shikonin via Receptor Interacting Protein Kinases in Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Cell Line, MCF-7.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(2):245-254. doi: 10.2174/1871520617666170919164055. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28933271
-
The natural anticancer agent plumbagin induces potent cytotoxicity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by inhibiting a PI-5 kinase for ROS generation.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45023. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045023. Epub 2012 Sep 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028742 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of plumbagin: Cytotoxic potential and pharmaceutical relevance towards cancer therapy.Food Chem Toxicol. 2019 Mar;125:566-582. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.01.018. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30685472 Review.
-
Anticancer Effects and Mechanisms of Action of Plumbagin: Review of Research Advances.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 1;2020:6940953. doi: 10.1155/2020/6940953. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33344645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery and cellular stress pathway analysis of 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives with novel, highly potent broad-spectrum anticancer activity.J Biomed Sci. 2018 Feb 8;25(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0408-6. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29422060 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin reduces human colon cancer cell survival by inducing cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.Int J Oncol. 2014 Nov;45(5):1913-20. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2592. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25109615 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and in vitro anti-proliferative evaluation of naphthalimide-chalcone/pyrazoline conjugates as potential SERMs with computational validation.RSC Adv. 2020 Apr 21;10(27):15836-15845. doi: 10.1039/d0ra01822h. eCollection 2020 Apr 21. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35493668 Free PMC article.
-
Antimutagenic and Synergistic Cytotoxic Effect of Cisplatin and Honey Bee Venom on 4T1 Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Cell Line.Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jan 29;2019:7581318. doi: 10.1155/2019/7581318. eCollection 2019. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30838042 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationship of anticancer drug candidate quinones.Turk J Chem. 2023 Dec 8;48(1):152-165. doi: 10.55730/1300-0527.3647. eCollection 2024. Turk J Chem. 2023. PMID: 38544901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powis G. Free radical formation by antitumor quinones. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1989;6:63–101. - PubMed
-
- Chen CH, Chern CL, Lin CC, Lu FJ, Shih MK, Hsieh PY, Liu TZ. Involvement of reactive oxygen species, but not mitochondrial permeability transition in the apoptotic induction of human SK-Hep-1 hepatoma cells by shikonin. Planta Med. 2003;69:1119–1124. - PubMed
-
- Li CJ, Wang C, Pardee AB. Induction of apoptosis by beta-lapachone in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3712–3715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
